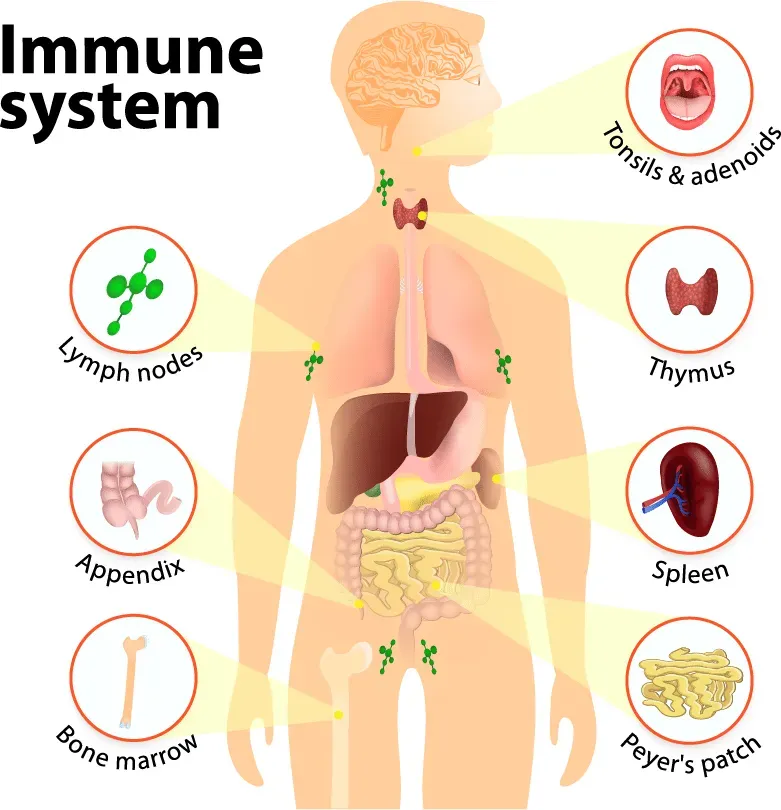
Immune Health is the foundation of how you respond to infections, recover from illness, and sustain daily energy. You don’t need a dramatic life overhaul to strengthen your immune system, because small, science-backed habits can yield meaningful improvements. By embracing a handful of simple, consistent practices—balanced nutrition, quality rest, regular movement, and good hygiene—you can support your body’s defenses and daily energy. A practical focus on sleep and immunity comes from daily routines that keep you resilient through seasonal challenges. Over time, small, steady changes—like choosing nutrient-dense foods, staying consistently active, and prioritizing hydration—add up to stronger natural defenses and greater everyday energy.
Beyond the phrase immune health, the idea embraces the body’s natural defenses and its coordinated immune response to pathogens. Researchers describe a two-tier system: innate barriers like skin and mucosal surfaces, and adaptive allies such as antibodies and memory cells. Supporting this resilience means supporting the function of white blood cells, maintaining a balanced inflammatory response, and ensuring that daily habits nurture a robust state of immunity. From a practical standpoint, people often focus on immune-boosting foods and other habits that support a healthy immune system. When these systems function well, you experience fewer disruptions from seasonal bugs and a steadier sense of wellness.
Immune Health Foundations: Nutrition That Supports Your Immune System
Immune Health starts with a strategic pattern of nourishment that feeds the immune system from the inside. Focus on a colorful plate that pairs fruits and vegetables with lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats to supply vitamins, minerals, fiber, and phytonutrients that support immune function. Immune-boosting foods include citrus fruits for vitamin C, fatty fish rich in omega-3s, fortified dairy or plant milks for vitamin D, zinc rich seeds and beans, and fermented foods that nurture a balanced gut microbiome that underpins immune responses.
A strong immune health is built over time through consistent eating patterns rather than chasing a single miracle ingredient. Prioritize high quality protein at each meal to supply amino acids for lymphocytes, antibodies, and other immune cells, and include probiotic foods like yogurt, kefir, miso, or sauerkraut to help balance the gut microbiome. Hydration supports mucosal barriers, while whole grains, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables provide minerals and phytonutrients that modulate inflammation and support lasting immune function.
Sleep and Immunity: The Nightly Ritual that Strengthens Your Immune System
Sleep and immunity are closely linked, and quality rest acts as a daily reset for immune defenses. When you sleep well, immune cells have time to repair and coordinate responses to pathogens, and chronic sleep loss can blunt this protection. Aim for seven to nine hours of sleep most nights and create a calm pre-sleep routine that signals your body to wind down. A cool, dark, and quiet room helps the body regulate hormones that influence immunity and recovery.
Make sleep a priority by limiting caffeine late in the day, turning off screens before bed, and maintaining a regular wake time even on weekends. If you struggle with rest, consider short breathing exercises, gentle stretching, or a brief mindfulness practice to shift your nervous system toward healing. Protecting sleep also supports daily energy and resilience against seasonal challenges to your immune system.
Move to Defend: Exercise and Immunity for Everyday Resilience
Regular moderate exercise is a proven ally for immunity. Activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing increase circulation of immune cells, helping them survey the body for invaders more efficiently. Consistency matters: aim for about 150 minutes of moderate activity per week and include two weekly strength sessions that support muscle mass and metabolic health, both of which underpin immune function.
Be mindful not to overdo it. Intense, prolonged workouts without adequate recovery can temporarily suppress immune responses and may elevate infection risk. Listen to your body, plan rest days, and tune your routine to your energy levels. For many people, a simple mix of daily movement, a couple of resistance sessions, and a longer weekly cardio session keeps the immune system primed without overreaching.
Stress Less, Shield More: Stress Management, Hydration, and Hygiene for Immunity
Chronic stress can hamper immune regulation, so adopting practical stress management techniques protects immune health. Practices like mindful breathing, short meditations, gentle yoga, or tai chi reduce perceived stress and help balance immune cell activity. Building small daily rituals—a five minute breathing pause or a gratitude journal—supports a calmer nervous system and more resilient immune responses.
Hydration, sunlight, and hygiene round out the basics of daily immunity. Drinking water keeps mucosal barriers hydrated, sunlight provides vitamin D creation in the skin, and regular hand washing with soap reduces exposure to pathogens. Staying current with vaccines and practicing good hygiene is a practical complement to the immune health habits discussed here, helping your body defend itself over time.
Planning Immune-Boosting Meals: A Colorful Plate for the Immune System
Planning meals with immune-boosting foods in mind creates a rainbow plate that fuels the immune system throughout the day. Include citrus or berries for vitamin C, fatty fish or fortified options for vitamin D and omega-3s, and a mix of plant proteins, nuts, and seeds for minerals like zinc and selenium. Fermented foods can support gut health, a key player in immune defense, while fiber from whole grains and vegetables feeds a diverse microbiome.
Think in a daily pattern: bright breakfasts with protein, colorful lunches and dinners, and snacks that balance carbs, protein, and fats. Use herbs and spices with anti-inflammatory properties to flavor meals and keep added sugars minimal to prevent metabolic stress. This approach helps you maintain steady energy and provides the nutrients your immune system relies on to function effectively when faced with seasonal challenges.
A Simple Daily Routine for Lasting Immune Health
A simple daily routine for lasting immune health centers on small, repeatable actions you can do every day. Start with a glass of water, a protein-rich breakfast, and a colorful fruit or vegetable component at every meal to supply vitamin C, zinc, and other immune-supporting nutrients. Regular movement and a short wind-down routine after sunset reinforce immune function and sleep quality, creating a durable foundation for health.
With consistency, the same core habits compound over weeks and months, strengthening your body’s defenses without requiring dramatic changes. Plan two to three days of moderate exercise, keep hydrated, practice stress reduction, and stay current with vaccines and hygiene practices. By making immune health a daily priority, you can improve energy, mood, and resilience to everyday pathogens.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Immune Health and how does it relate to the immune system in everyday life?
Immune Health is the foundation of how your immune system responds to infections and recovers from illness in daily life. To support immune health, focus on practical steps: eat a pattern of immune-boosting foods, get adequate sleep, move regularly, manage stress, and practice good hygiene. These small, sustainable choices strengthen the body’s defenses over time.
Which immune-boosting foods should I include to support Immune Health?
Immune-boosting foods are not a single miracle fix but a pattern of eating that provides vitamins, minerals, fiber, and healthy fats to nourish the immune system. Include citrus fruits, berries, leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, fatty fish, beans, and fermented foods to cover nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, selenium, and omega-3s. Probiotic foods like yogurt or kefir can support gut health, which is linked to immune function.
How does sleep affect immunity and Immune Health?
Most adults benefit from 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night; better sleep supports immunity and recovery. Maintain a consistent schedule, create a calming pre-sleep routine, and optimize your sleep environment (dark, cool, quiet). Reducing late-day caffeine and limiting screen time can improve sleep quality, which in turn supports immune health.
What role does exercise play in immunity for Immune Health?
Regular moderate exercise improves circulation of immune cells and supports immune regulation. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity weekly, plus two strength-training sessions; choose activities you enjoy like walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing. Avoid overtraining, listen to your body, and incorporate rest days to prevent temporary immune suppression.
How can stress management support Immune Health and the immune system?
Chronic stress can dampen immune responses, but stress management strategies can protect Immune Health. Practices such as mindful breathing, short meditations, yoga, or tai chi reduce perceived stress and support immune regulation. Social connection, even brief check-ins with friends, also buffers stress and supports immune health.
Why is hygiene and vaccination important for Immune Health?
Hygiene and vaccination are practical cornerstones of immune health. Regular hand washing, avoiding touching the face, and staying up to date with vaccines reduce exposure to pathogens and support the immune system. Hygiene is a complement to a strong immune system, not a substitute for healthy habits like nutrition, sleep, and physical activity.
| Aspect | Key Point | Practical Tips |
|---|---|---|
| What Immune Health Is | Foundational to how you respond to infections, recover from illness, and sustain daily energy. | Adopt consistent, science-aligned habits; focus on small, regular improvements over time. |
| Nutrition & Immune Health | A broad pattern of eating provides vitamins, minerals, fiber, and healthy fats to support immune function. | Eat a variety of fruits/vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and fermented foods; include citrus, berries, leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, and fatty fish; consider fortified foods if vegan/vegetarian. |
| Key Nutrients | Vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, selenium, and omega-3 fatty acids support immune defenses and regulation. | Plan meals to meet these nutrients; if vegan/vegetarian, ensure sources of zinc and vitamin D; discuss supplements with a healthcare provider if needed. |
| Protein & Probiotics | Protein supports immune cell production; probiotics support gut health and microbiome balance. | Include high-quality protein at every meal (eggs, dairy or fortified plant milks, beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, lean meats); add probiotic foods with live cultures. |
| Hydration & Balanced Meals | Water supports mucosal barriers; balanced meals sustain energy and immune function. | Colorful plates: combine carbs, protein, and healthy fats; include citrus/berries, leafy greens, whole grains, and a protein source at each meal. |
| Sleep & Immunity | Adequate sleep strengthens immune function and recovery. | Adults typically need 7–9 hours; maintain a regular schedule, calming pre-sleep routine, and a sleep-friendly environment. |
| Exercise & Immunity | Regular moderate activity improves circulation of immune cells and supports overall health. | Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate activity weekly; include strength training; listen to your body and allow recovery. |
| Stress Management | Chronic stress can dampen immune responses; managing stress supports immune regulation. | Practice mindful breathing, short meditations, gentle movement, journaling, and maintain social connections. |
| Hygiene, Sunlight & Vaccines | Hygiene reduces exposure to pathogens; sunlight and vaccines support immune regulation. | Wash hands, avoid touching face, stay up to date with vaccines; seek sensible sun exposure and consider vitamin D sources if deficient. |
| Daily Routine | A simple, sustainable routine makes immune health easier to maintain. | Start with water at breakfast, colorful meals, regular movement, wind-down routine for sleep, stress management, and hygiene habits. |
Summary
Table of key points: The table above summarizes core areas affecting Immune Health, including nutrition, key nutrients, protein & probiotics, hydration, sleep, exercise, stress management, hygiene, sunlight, vaccines, and building a simple daily routine. Each row provides a concise takeaway and actionable tips to support immune function through everyday choices.