Customer-centric business thinking places the customer at the center of every decision, shaping products, services, and experiences, and this mindset informs product roadmaps, pricing choices, and brand messaging across channels. When you align operations around customer needs, you don’t just close deals—you build relationships that fuel growth, a core element of effective customer retention strategies. By treating the customer experience as a strategic asset, you empower teams across marketing, sales, and support to deliver consistent value. A customer-first approach guides every interaction, helping you delight customers and strengthen client retention over time, while fostering trust and advocacy. This article outlines practical, actionable steps to embed this mindset into culture, operations, and strategy.
With a customer-focused mindset, organizations reposition success around the end-user, prioritizing long-term relationships over one-off transactions. Instead of chasing short-term boosts, teams map the customer journey, listen to feedback, and optimize every touchpoint to improve loyalty and lifetime value. A client-first orientation translates into coherent experiences—from onboarding to renewal—where every department shares a common goal: satisfy and empower customers. By centering value delivery, businesses cultivate trust, advocacy, and sustained engagement that drive growth beyond isolated campaigns.
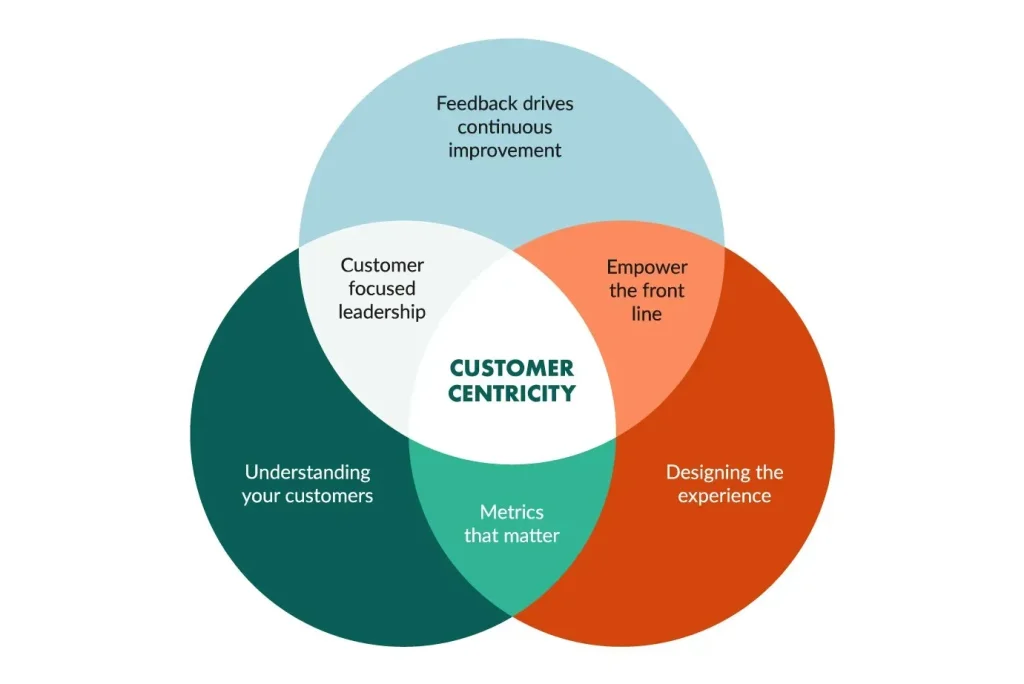
Becoming a Customer-Centric Business: Align Strategy, Culture, and Metrics
In a competitive market, becoming a customer-centric business means placing customer outcomes at the center of strategy, decision-making, and investment. It isn’t just about winning a sale; it’s about building durable relationships that fuel sustainable growth through a focused customer experience and a true customer-first approach.
To operationalize this mindset, document a clear customer value proposition and cascade goals across teams, creating cross-functional ownership of the experience. When leadership signals that the customer is the ultimate arbiter of success, it sets the stage for effective customer retention strategies and stronger client retention over time.
Mapping the Customer Journey to Reduce Friction and Improve Client Retention
A comprehensive map of the end-to-end journey—from discovery to advocacy—highlights moments that influence satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term retention. By integrating voice-of-customer data and key metrics like CSAT, NPS, and CES at each stage, you reveal friction points that erode the customer experience.
Practical steps include proactive onboarding, transparent communication, and seamless handoffs between sales, onboarding, and support. These moves are classic elements of client retention strategies and contribute to a smoother, more delightful journey.
Delighting Customers: Delivering Consistent, Tangible Value at Every Touchpoint
Delighting customers isn’t about one-off perks; it’s about delivering consistent value that aligns with goals and reduces effort. When every interaction adds tangible benefit, you strengthen the customer experience and set the stage for renewal and advocacy.
Strategies to delight customers include personalization at scale, fast, reliable support across channels, anticipatory service, and thoughtful touches that celebrate milestones. These practices reinforce a customer-centric mindset and drive durable client retention.
Elevating the Customer Experience Across Channels and Touchpoints
The customer experience is the sum of all interactions with your brand. Elevating CX requires consistent branding, accessible support, and rapid, accurate responses across channels to minimize confusion and friction.
Integrating multichannel support with unified data ensures agents can resolve issues quickly while maintaining a coherent experience. By prioritizing accessibility and inclusivity, you broaden engagement and protect long-term client retention.
The Customer-First Approach: Personalization, Context, and Proactive Support
A customer-first approach treats each interaction as unique while operating at scale. Personalization isn’t guesswork; it’s using context, goals, and history to tailor recommendations and experiences that advance customer outcomes.
Tactics include segmented onboarding, contextual communications triggered by behavior, and ongoing experimentation through A/B testing and feedback. This approach strengthens the customer experience and supports stronger client retention.
Measuring Success with Retention-Focused KPIs and Feedback Loops
To prove that a customer-centric strategy is working, track the right metrics: CSAT, CES, NPS for advocacy, churn and renewal rates for retention, and CLTV for long-term value. When these indicators trend positively, you can attribute improvements to concrete retention strategies.
Close the loop by collecting feedback, analyzing root causes, implementing fixes, and communicating improvements back to customers. A closed-loop process—combined with quarterly business reviews and visible changes—converts insights into ongoing client retention and trust.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does it mean to be a customer-centric business in today’s market?
A customer-centric business places customer needs and outcomes at the center of strategy and operations, prioritizing the customer experience and adopting a customer-first approach. It means listening with empathy, aligning teams around shared customer goals, and designing products, services, and interactions to solve real problems. The result is higher satisfaction, reduced churn, and increased lifetime value.
What are effective customer retention strategies for a customer-centric business?
Implement customer retention strategies by mapping the full journey and building onboarding, activation, and renewal processes that deliver consistent value. Use proactive engagement, regular value checks (QBRs), and health scoring to identify at-risk accounts early. Track churn, renewal rate, and CLTV to drive continuous improvement.
How can we delight customers in a customer-centric business?
Delight customers through personalization at scale, fast and empathetic support, proactive problem solving, and thoughtful touches such as milestone celebrations and relevant, timely communications. Anticipate needs and remove friction across the onboarding and usage journey.
How does improving the customer experience support a customer-centric business?
The customer experience is the sum of all interactions with your brand. Strengthen CX with consistent branding across channels, multichannel support, quick and accurate responses, and accessible experiences. Collect feedback, close the loop, and visibly show how improvements benefit customers.
How should a customer-first approach influence product strategy and cross-functional alignment?
A customer-first approach drives product strategy by focusing on outcomes customers seek, guiding pricing and roadmaps around real needs, and cascading customer goals into department objectives. It also fosters cross-functional ownership of the end-to-end experience and leadership visible commitment to customer success.
What metrics matter when measuring client retention and a customer-centric strategy?
Key metrics include client retention measures (churn, renewal rate, CLTV), as well as customer experience indicators (CSAT, CES) and advocacy (NPS). Use a closed-loop process: collect feedback, investigate root causes, implement fixes, and communicate improvements to customers to reinforce trust.
| Theme | Core Idea | Practical Actions |
|---|---|---|
| What it means to be customer-centric? | Prioritizes customer needs and outcomes over internal convenience; sustained discipline across product, sales, marketing, support, and finance. | – Listen deeply; – Design products/services to solve real problems; – Use customer feedback and data to inform decisions; – Align goals and incentives around customer outcomes. |
| Centering the customer in strategy | Start with a clear value proposition that resonates with real customer needs; align all teams; leadership communicates the customer as the ultimate arbiter of success. | – Define valuable customer segments; – Identify outcomes and barriers; – Shape product roadmap, pricing, and messaging; – Cascade goals; – Leadership signals customer success as a metric. |
| Mapping the customer journey | Map the end-to-end journey from awareness to advocacy; identify friction and collect voice-of-customer data; monitor key metrics. | – Chart stages (discovery, onboarding, usage, renewal, advocacy); – Collect VOC data; – Identify friction points; – Remove onboarding friction; – Ensure fast, empathetic support; – Use CSAT/NPS/CES metrics. |
| Delighting customers with consistent value | Deliver value that aligns with customer goals and reduces effort; focus on consistency over one-off perks. | – Personalization at scale; – Fast, reliable multi-channel support; – Anticipatory service; – Thoughtful touches (milestones, upgrades) |
| The role of the CX | Customer experience is the sum of all interactions; optimize with a closed-loop feedback system. | – Consistent branding across channels; – Multichannel support with unified data; – Speed and accuracy; – Accessibility and inclusivity. |
| Personalization and the customer-first approach | Treat interactions as unique, while operating at scale; use context/history to inform recommendations. | – Segmented onboarding; – Contextual communications; – Data-driven optimization; – A/B testing and feedback loops. |
| Retention through engagement and value delivery | Ongoing perceived value and ease reduce churn; implement retention playbooks. | – Regular value checks (QBRs); – Proactive health scoring; – Clear ROI demonstrations; – Loyalty/advocacy programs. |
| Building a customer-centric culture across the organization | Culture and leadership must model customer focus and empower teams. | – Leadership example; – Cross-functional alignment; – Employee empowerment; – Customer-outcome metrics; – Continuous learning. |
| Measuring success: metrics that matter for a customer-centric business | Use key metrics to prove impact and drive improvements. | – CSAT, CES, NPS, CLTV, TTV; – Closed-loop feedback; – Data-driven optimization; – Communication of improvements to customers. |
Summary
A customer-centric business begins with a clear mindset and a system that places customers at the heart of strategy, decisions, and operations. By mapping journeys, delivering consistent value, personalizing experiences, and measuring outcomes, it can reduce churn, increase lifetime value, and build lasting loyalty. Achieving this requires leadership commitment, cross-functional collaboration, and a culture of continuous learning that listens to customers and acts on their feedback.