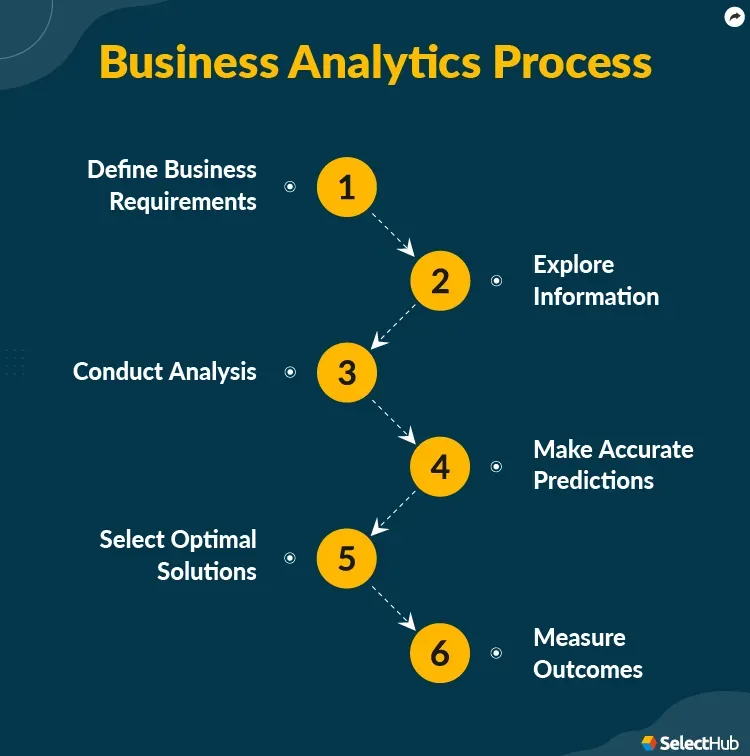
Business Analytics reshapes how organizations turn data into revenue by guiding decisions with evidence, discipline, and timely insights. In a world flooded with signals from marketing, sales, product, and service interactions, data-driven decision making acts as the compass that keeps strategy aligned with real outcomes. An effective analytics program translates complex data into clear actions through data visualization, intuitive dashboards, and focused metrics that matter to revenue. When analytics are connected to explicit business goals, teams can observe how changes in pricing, onboarding, or messaging influence CAC, LTV, and conversion rates. This primer highlights pathways to greater revenue impact by building data literacy, governance, and an analytics culture that puts evidence at the center of decision making.
From a strategic analytics perspective, organizations explore how data-informed insights drive profitability and competitive advantage. The field can also be described as business intelligence and data science applied to operations, marketing, and customer experience to shape actionable plans. By turning numbers into narratives, teams harness predictive analytics and data visualization to forecast outcomes, optimize investments, and guide executive choices.
Align Analytics with Revenue Goals to Drive Revenue-Linked Decisions
Anchor your analytics program to revenue goals by defining a small, focused set of metrics—CAC, LTV, ARPU, conversion rates, churn—and map every data source to those metrics. This alignment bridges data collection with concrete actions, enabling data-driven decision making as marketing touchpoints, product changes, and sales initiatives are tied to measurable revenue outcomes. Use data visualization and dashboards to surface the exact levers that move revenue, so executives and frontline teams share a common view of performance. In practice, this revenue-centric alignment makes analytics more than reporting; it becomes a language for prioritizing bets that improve ROI optimization.
With revenue anchors in place, teams can analyze how each function influences the funnel. Marketing attribution models, product usage signals, and renewal probabilities reveal which activities drive conversions and where revenue is at risk. This clarity reduces guesswork and accelerates decision cycles, turning insights into action. The goal is to integrate analytics across marketing, sales, and product so that data-driven decisions permeate every initiative, from campaign design to pricing experiments, ensuring that every action is measured against the same revenue yardstick.
Construct a Revenue-Focused Analytics Stack for Actionable Insights
Design a purpose-built analytics stack that collects data from CRM, marketing automation, ecommerce, and product analytics, then processes it through ETL or ELT pipelines into a centralized analytics layer. The stack should feed a data warehouse or data lake, with a BI layer that translates raw numbers into meaningful visuals and dashboards. By centering the stack on revenue metrics—CAC, LTV, ARPU, renewal rates—business intelligence tools illuminate the health of the pipeline and the drivers of revenue. Self-service analytics empower marketers and product managers to explore questions without waiting for data scientists, speeding time-to-insight and reducing friction in decision making.
Establish governance that covers data lineage, versioning, security, and ownership. A lean architecture that emphasizes clean, joined data from mission-critical sources (CRM, billing, product usage) reduces bottlenecks and ensures trustworthy insights. When data is reliable, dashboards and data visualizations reflect reality, enabling teams to test hypotheses and tune actions with confidence. The result is a scalable foundation where data-driven decision making becomes habitual rather than exceptional.
Business Analytics: From Descriptive to Prescriptive for Revenue Optimization
Business Analytics encompasses descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, each layer adding revenue value. Descriptive analytics show what happened; diagnostic reveals why; predictive estimates what will happen; prescriptive recommends specific actions to influence outcomes. Together they form a pipeline that moves from history to action, catalyzing revenue optimization. Use predictive analytics to forecast churn risk, forecast demand, and identify price elasticity opportunities, while prescriptive recommendations translate those forecasts into concrete campaigns and experiments. Data visualization plays a key role in communicating model outputs to business stakeholders and aligning on next steps.
Real-world use cases demonstrate ROI: churn reduction through targeted onboarding changes, pricing experiments guided by elasticity models, and win-back campaigns informed by customer lifecycle insights. By integrating these analytics stages into a cohesive strategy, organizations shift from intuition-based decisions to evidence-based bets. The result is a more resilient revenue engine where Business Analytics informs prioritization, allocation of resources, and continuous improvement of go-to-market motions.
Data Quality, Governance, and Trusted Insights
Data quality is the oxygen of analytics. Start with data quality rules, data owners, and repeatable ETL that cleans, joins, and syncs CRM, billing, product usage data into a centralized analytics layer. This ensures that dashboards and data visualizations rest on accurate, timely data, which strengthens data-driven decision making across teams. Governance should address data lineage, version control, and security to prevent drift and unauthorized access while preserving flexibility for experimentation.
With trusted data, analysts can focus on analysis rather than wrangling. Clear ownership and documented data lineage enable faster audits and easier collaboration with business units. A robust governance framework supports compliance and risk management, while enabling self-service analytics that still adheres to standards. In this environment, business intelligence becomes a trusted partner in steering revenue strategy rather than a backlog of stale reports.
Practical Revenue Use Cases: Marketing Attribution, Pricing, and Churn
Marketing attribution demonstrates how revenue results emerge from multiple interactions, not a single campaign. A multi-touch attribution approach models touchpoints and their contributions to revenue, guiding ROI optimization of marketing spend. Use data visualization to present channel mix, attribution results, and incremental lift in revenue, making the rationale for budget shifts clear to stakeholders. Pair attribution with predictive analytics to anticipate which channels will yield the best payoffs under different scenarios.
Other high-impact use cases include pipeline forecasting, territory performance analysis, win-rate optimization, and pricing and revenue management driven by elasticity models. These analyses help protect gross margin while maximizing revenue, and help uncover opportunities for upsell and cross-sell by analyzing product usage patterns and customer segments. The combination of descriptive dashboards and predictive models supports proactive interventions to extend customer lifetime value and reduce churn.
Fostering Data Literacy and a Culture of ROI-Driven Analytics
Beyond technology, culture matters. Invest in people and processes that improve data literacy and collaboration between data teams and business units. Assign data asset ownership, establish regular reviews of key revenue metrics, and create rituals for data-informed decision making. When teams routinely test hypotheses and share learnings, data-driven decision making becomes embedded in operations and strategy, not an afterthought.
Leadership plays a critical role in modeling data-driven behavior and enabling analysts to push insights into action. Track ROI of analytics initiatives by tying projects to concrete revenue outcomes such as increased conversion, higher LTV, or reduced CAC. As the organization scales, expand analytics capabilities to more advanced models, scenario planning, and optimization techniques, reinforcing the link between analytics and sustainable revenue growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can Business Analytics align analytics with revenue goals to strengthen data-driven decision making?
Start by anchoring your Business Analytics program to a small set of revenue metrics (for example CAC, LTV, ARPU, conversion rate, churn) and map every data source to those metrics. This connects data collection to actions that move revenue, enabling data-driven decision making across marketing, sales, and product. Ensure data quality and governance so insights are trusted, and design the analytics workflow to drive ROI optimization with measurable, revenue-driven outcomes.
Why are data quality and governance essential in Business Analytics to support reliable insights and predictive analytics?
Data quality and governance are the oxygen of Business Analytics. Assign data owners, define quality rules, and implement data lineage, versioning, and security. With clean, trusted data, teams can rely on descriptive and diagnostic insights and power predictive analytics to forecast outcomes, accelerating decision making and supporting ROI optimization.
How do data visualization and business intelligence tools support revenue-focused decision making in Business Analytics?
In Business Analytics, data visualization and business intelligence tools translate data into meaningful visuals and dashboards. A purpose-built analytics stack (CRM, marketing automation, e-commerce, and product analytics, plus ETL/ELT, a data warehouse or lake, and a BI layer) enables self-service analytics and reveals revenue-focused insights like funnel health and attribution, helping stakeholders act quickly and improve ROI.
What are the four analytics stages in Business Analytics and why do they matter for ROI optimization?
Descriptive analytics answers what happened; diagnostic analytics explains why it happened; predictive analytics estimates what will happen; prescriptive analytics recommends actions to influence outcomes. In Business Analytics, moving through these stages adds value and drives ROI optimization by turning insights into concrete revenue actions.
Can you give examples of revenue-focused use cases in Business Analytics and how they drive ROI optimization?
Practical use cases illustrate the value of Business Analytics: marketing attribution models that credit across touchpoints, pipeline forecasting and win-rate analysis from sales analytics, and pricing and revenue management using elasticity insights. Across these areas, predictive analytics and data visualization help optimize ROI and guide revenue strategy.
What practical steps should organizations take to implement a revenue-centric Business Analytics program?
Start with governance and data quality as the foundation, then build a lean analytics stack focused on revenue metrics. Create a prioritized analytics roadmap, foster data literacy and collaboration between data teams and business units, and cultivate a culture of data-driven decision making. Finally, measure ROI by linking analytics projects to revenue outcomes and iterate based on results.
| Topic | Key Points | Examples / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Anchor analytics to revenue goals | Define revenue-centric metrics; map data sources to metrics (CAC, LTV, ARPU, conversion, churn, deal size, renewal) | Align marketing, product, and sales actions to revenue results; foundation of data-driven decisions. |
| Data quality & governance | High-quality data; data owners; data quality rules; governance (lineage, versioning, security) | Start with CRM, billing, product usage; implement repeatable ETL to a centralized analytics layer; trusted data speeds insights. |
| Analytics stack design | Data sources (CRM, marketing automation, ecommerce, product analytics); ETL/ELT; data warehouse/lake; BI layer; self-service | Dashboards show funnel, pipeline health, and attribution; self-service analytics reduces bottlenecks. |
| Analytics maturity | Descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, prescriptive analytics; each adds value | Descriptive: what happened; Diagnostic: why; Predictive: what will happen; Prescriptive: suggested actions. |
| Revenue-focused use cases | Marketing attribution; Sales analytics; Pricing & revenue management; Customer lifecycle; Upsell/cross-sell | Model touchpoints; pipeline forecasting; elasticity; churn interventions; lifetime value improvement. |
| Implementation plan | Governance & data quality as foundation; lean analytics stack; prioritized roadmap; invest in people & processes; data literacy & collaboration | Cross-team collaboration; quick wins plus longer-term capability; governance framework. |
| Culture & governance | Culture matters; data literacy; clear data ownership; regular reviews; rituals; leadership support; empower analysts | Agile decision-making and a data-informed culture. |
| ROI & Measurement | Measure ROI by revenue outcomes; track time-to-insight; expand capabilities; optimize risk | Tie projects to revenue outcomes; demonstrate value over time. |
Summary
Business Analytics is a powerful engine for turning data into actionable revenue. By aligning analytics with revenue goals, ensuring data quality, building a robust analytics stack, and fostering a culture that embraces data driven decision making, organizations can unlock meaningful growth. The journey from data to revenue is iterative and collaborative, requiring clear governance, practical analytics use cases, and a willingness to test and refine. When teams rely on insights to guide strategy and execution, revenue opportunities become more predictable and scalable.