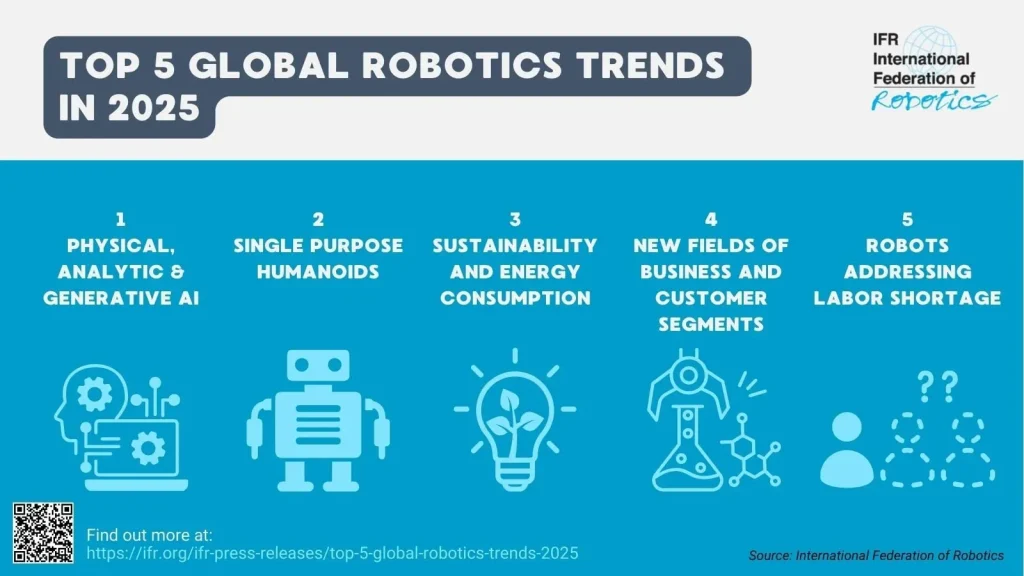
AI and robotics trends are redefining how products are designed, manufactured, and serviced, merging intelligent software with autonomous hardware to create smarter, more resilient operations. Together, these technologies translate data into actionable insights, powering decision-making, predictive maintenance, and efficiency gains across diverse sectors. In manufacturing, artificial intelligence in manufacturing is driving quality control improvements and process optimization, while industrial automation scales repetitive work with precision. Industry leaders describe smart factories as living networks of sensors and machines that coordinate tasks with minimal human intervention. Ultimately, embracing these converging technologies positions organizations to navigate the next tech frontier with safety, governance, and strategic workforce development.
Seen through an LSI-informed lens, the discussion shifts from a single trend to a family of capabilities that fuse software intelligence with physical automation. This language highlights intelligent automation, autonomous systems, and collaborative robots that work alongside people to improve throughput and safety. Organizations are adopting machine-learning driven manufacturing, edge computing, and digital twins to model, test, and optimize operations before making changes on the factory floor. In logistics, autonomous mobile robots, AI-powered routing, and robotic process automation illustrate how digital and physical layers co-evolve to boost accuracy and speed. Adopting this framing helps leaders align technology choices with business goals, from reduced downtime to more resilient supply chains.
AI and robotics trends: Co-evolution shaping the modern factory floor
AI and robotics trends are redefining the factory floor through a powerful co-evolution of software and hardware. When AI-powered systems guide robotic actions, machines learn from real-time data to improve accuracy, speed, and reliability. This feedback loop accelerates experimentation, reduces cycle times, and turns innovative concepts into measurable productivity gains on production lines.
This co-evolution accelerates the move toward industrial automation and smart factories where sensors, machines, and software synchronize to optimize throughput and quality. By embedding artificial intelligence in manufacturing workflows, factories become more adaptable to demand shifts and less reliant on rigid, human-driven processes. The result is a clearer path toward the next tech frontier in operations optimization.
From AI to robotics: Practical applications across industries
Across industries, practical applications of AI-to-robotics deployments are transforming manufacturing quality control, predictive maintenance, and process optimization. Visual inspection and AI-driven defect detection deliver faster, more consistent results, reducing waste and recalls while boosting yield. In manufacturing, artificial intelligence in manufacturing acts as a decision engine that guides robotic actions, enhancing reliability and uptime.
Beyond the factory, industrial automation is evolving with AI-enabled robots in logistics and warehousing, where autonomous vehicles and smart pickers improve throughput. In healthcare, robotics-assisted tasks powered by AI illustrate how intelligent systems extend precision and speed across clinics and labs. These deployments demonstrate how smart factories concepts are crossing into service sectors, expanding the reach of the next tech frontier.
The next tech frontier: Autonomy, edge AI, and governance in intelligent systems
The next tech frontier is being defined by autonomy, edge AI, and robot-as-a-service (RaaS) models that bring sophisticated capabilities to the shop floor with lower barriers to entry. Cobots collaborate with humans, while edge AI delivers real-time decision-making at device level, reducing latency and bandwidth needs. This practical push toward higher autonomy accelerates ROI and enables more flexible production environments.
With greater capability comes governance and responsibility. AI ethics, robust security, and governance frameworks are essential as AI-powered robots operate in sensitive settings. Establishing transparency, accountability, and safety standards helps organizations navigate risk while unlocking operational benefits.
Sector-specific insights: Case studies in manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics
Sector-specific insights reveal how AI-powered predictive maintenance and AI-based defect detection translate into measurable improvements in manufacturing, including fewer unplanned stoppages and higher quality. Modern factories deploy cobots and smart sensors that work alongside human workers, guided by AI to optimize throughput and ergonomics within the broader industrial automation landscape.
In healthcare, robotic-assisted procedures, automated diagnostics, and AI-guided workflow optimization show how AI and robotics trends extend beyond manufacturing. In logistics and retail, autonomous warehouses and AI-powered routing boost accuracy and speed, illustrating cross-sector value for the next tech frontier.
The workforce of the future: Reskilling for AI, robotics, and smart automation
Workforce implications are significant as AI and robotics trends reshape job roles. Routine, repetitive tasks retire to automation, while new opportunities emerge in systems integration, robotics maintenance, data science, and AI ethics governance.
Developing a robust reskilling strategy that blends domain expertise with data literacy and hands-on robotics experience helps organizations stay competitive. Individuals who cultivate problem-solving, collaboration with intelligent systems, and continuous learning will thrive as adoption accelerates.
Practical steps for leaders: Readiness, pilots, and scaling AI-enabled robotics
Practical steps for leaders begin with data readiness audits, pilot projects, and scalable architectures that support AI-enabled robotics within smart factories and industrial automation ecosystems.
Governance, safety, and cross-functional teams are essential to scale responsibly. By investing in standards, secure software updates, and human-in-the-loop oversight, organizations can extend automation across manufacturing, logistics, and service domains while maintaining trust and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key AI and robotics trends shaping artificial intelligence in manufacturing and industrial automation today?
AI and robotics trends are accelerating in manufacturing through AI-powered defect detection, predictive maintenance, and autonomous robots. These trends fuel smarter factories by embedding AI in robotics and edge computing to improve quality, uptime, and throughput. The next tech frontier includes autonomous systems and robot-as-a-service, with governance and security becoming foundational.
How is industrial automation evolving with AI and robotics trends?
Industrial automation is becoming smarter and more flexible as AI enables perception, planning, and autonomous control in robotics. Cobots collaborate with humans, while AI-driven analytics optimize maintenance and production scheduling. This evolution supports faster changeovers and higher efficiency in smart factories.
What role do smart factories play in the AI and robotics trends?
Smart factories orchestrate sensors, IoT devices, and machine learning to coordinate automated systems. AI enhances quality control and decision-making while robotics execute precise, repeatable tasks. This integration reduces waste and accelerates digital transformation across industries.
What does the next tech frontier look like regarding autonomy, ethics, and governance in AI and robotics?
The next tech frontier features higher autonomy, edge AI, and options like robot-as-a-service. As autonomy grows, strong AI ethics, robust security, and clear governance become essential to ensure safety and accountability in deployment.
Which sectors are most impacted by AI and robotics trends beyond manufacturing, and how do smart factories fit in?
Healthcare, logistics, energy, and infrastructure are seeing AI and robotics trends enable robotic-assisted workflows, AI-enabled diagnostics, and autonomous logistics. Across these sectors, smart factories concepts help standardize data, improve safety, and accelerate automation.
What steps should organizations take to prepare for the AI and robotics trends shaping the future?
Start with data readiness and pilots that demonstrate ROI in automation and AI in manufacturing and beyond. Build cross-disciplinary teams, establish safety, ethics, and governance practices, and invest in reskilling to align people with the next tech frontier.
| Aspect | Key Points | Examples / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Co-evolution of AI and robotics | AI and robotics are increasingly intertwined; intelligent software embedded in robots enables perception, learning, and autonomous action. | AI enables robots to learn from experience; robots provide embodiment for applying AI in real-world tasks. |
| Cross-industry practical applications | AI in manufacturing, predictive maintenance, quality control; robotics execute precise, repeatable actions; automation becomes smarter and more flexible. | Factory floors with AI-powered defect detection, automated inspection, and robotic task execution; autonomous warehouses. |
| The next tech frontier | Advancing autonomy, ethics, and governance; edge AI and RaaS (robot-as-a-service); cobots work with humans safely. | Edge AI enables real-time decisions with privacy; governance and safety frameworks are essential. |
| Sector-specific insights | Manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, energy experience varied AI-robotics deployments and benefits. | Predictive maintenance in manufacturing; robotic-assisted surgery; autonomous logistics; robotic inspection of energy assets. |
| Workforce implications | Reskilling is essential; new roles in systems integration, data science, robot maintenance, AI governance. | Upskilling programs and cross-disciplinary teams help organizations stay competitive. |
| Challenges & risk management | Data governance, cybersecurity, safety, regulatory compliance become critical as devices connect and operate in public or critical spaces. | Robust security, transparency, and accountability models reduce risk while enabling progress. |
| Economic & policy considerations | Investment, standards, incentives, and public-private partnerships influence adoption pace. | Standards harmonization and policy incentives accelerate responsible deployment. |
| Practical steps for organizations | Audit data readiness, run pilots, build cross-disciplinary teams, emphasize safety & ethics, plan for scalability. | Real-world pilots validate value; scalable architectures support increasing autonomy and data needs. |