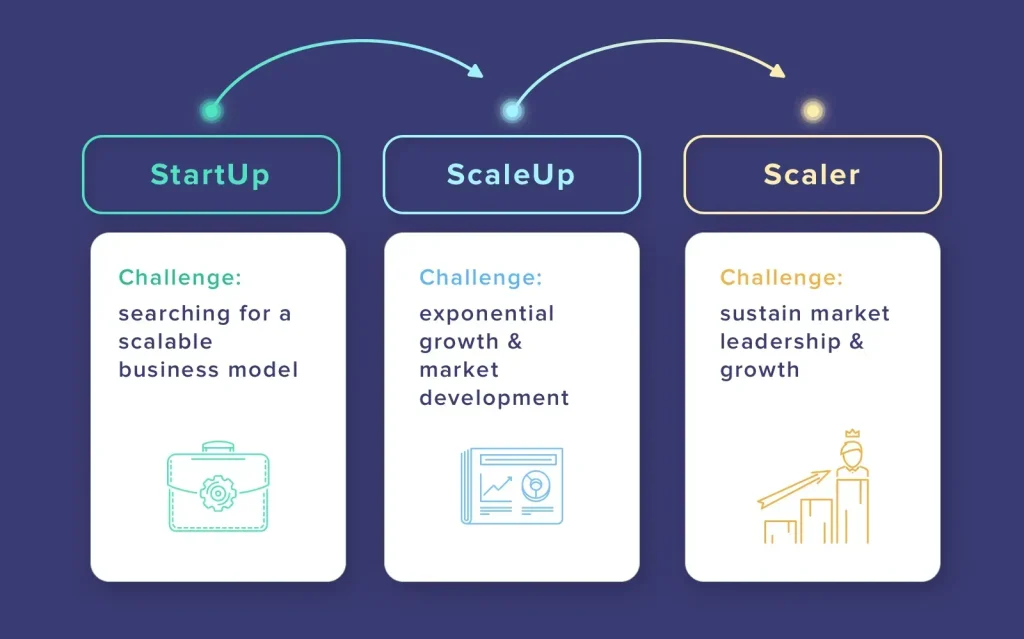
Startup to Scaleup Growth represents the intentional transition from the nimble, experiment-driven phase of a new venture to a structured, metrics-backed engine of sustainable expansion, where founders must reconcile vision with governance, capital discipline, and scalable operating rhythms, setting the tone for strategic bets that endure through market cycles. In practice, this journey follows a clearly defined growth lifecycle, guiding you from discovery and early product-market fit toward repeatable demand generation, scalable delivery, and the governance frameworks that sustain velocity without sacrificing quality or customer value in diverse markets and evolving competitive landscapes. A disciplined startup growth strategy anchors decisions around pricing, packaging, and early GTM bets, ensuring that each experiment builds toward a repeatable model while preserving the entrepreneurial edge that initially attracted customers and investors globally. As you scale, mastering scaling a startup means designing systems that can flex with demand, establishing growth-stage metrics that illuminate unit economics, customer health, and channel effectiveness, and aligning talent, culture, and incentives with a long-term trajectory. Founders who lean into venture scaling strategies, coupling capital allocation with disciplined experimentation and continuous learning, can maintain urgency and curiosity while delivering on the promise of durable growth that compounds value for customers, employees, and stakeholders, for today and tomorrow.
Viewed through an expansion lens, the transition from a founder-led startup to a scale-ready organization hinges on repeatable processes, disciplined execution, and a culture that can sustain momentum as complexity grows. This progression is often framed in terms of scaling, growth acceleration, and the establishment of governance structures that translate early traction into durable profitability. Leaders focus on signals such as recurring revenue, customer health, product-market fit durability, and efficient operations, while teams expand capabilities across product, sales, marketing, and customer success to reach larger markets. By laying out clear milestones, revenue predictability, scalable delivery, and capital discipline, organizations keep the long-term value proposition in sight and avoid sacrificing the entrepreneurial energy that sparked initial growth.
Startup to Scaleup Growth: Navigating the Growth Lifecycle Milestones
Embarking on Startup to Scaleup Growth requires a clear map of the growth lifecycle. Founders must translate early learnings into scalable playbooks that align product, market, and capital for sustainable velocity, shaping a practical startup growth strategy.
By embracing a structured growth lifecycle, you reduce guesswork, anticipate bottlenecks, and accelerate toward long-term profitability. This approach preserves the nimble ethos that sparked initial momentum while introducing governance, repeatability, and a disciplined cadence around metrics and learning.
From Product-Market Fit to Repeatable GTM: Building a Scalable Growth Engine
The Transition from Startup Foundations to Growth at Scale marks moving from product-market fit exploration to a repeatable GTM engine—the core of scaling a startup. This stage is the practical realization of a disciplined startup growth strategy and a shift from experimentation to systematized execution.
This phase requires a defined pricing model, clear onboarding, and repeatable sales processes. Start tracking early cohort-level metrics such as CAC, LTV, churn, and payback period to validate unit economics and lay the groundwork for a durable growth engine.
Scaling Organization, Culture, and Governance for Sustainable Growth
As growth becomes more predictable, Stage 3 focuses on scaling organization, culture, and governance to support increasing complexity. Building the operating backbone—finance, HR, IT, and customer success—ensures the company can handle a larger, more diverse customer base.
Key actions include designing an org structure that aligns with growth, implementing scalable product development and customer support processes, and instituting governance mechanisms like OKRs, quarterly planning, and leadership development to sustain velocity with quality.
Measuring Growth: Growth-Stage Metrics and Data-Driven Decisions
Stage 4 hinges on robust measurement—growth-stage metrics and dashboards that translate activity into actionable insight. Real-time visibility helps leadership diagnose issues early and steer investments toward the most impactful initiatives.
Core metrics to monitor include revenue run rate by segment, CAC payback, gross margin, churn, net revenue retention, and operational indicators such as burn rate and cash runway. These metrics guide product iterations, marketing investments, and resource allocation across the scale.
Venture Scaling Strategies: Aligning Capital, Talent, and Product Roadmaps
Stage 5 is where venture scaling strategies come into play. Avoid common slips by ensuring the growth model remains capital-efficient, governance-focused, and tightly aligned with the core value proposition as you expand.
This phase also emphasizes planning for the next wave: building a leadership bench, accelerating talent development, and mapping a roadmap that coordinates product, sales, and customer success with funding milestones.
Practical Playbooks for Long-Term Scale: Avoiding Pitfalls and Maintaining Velocity
Stage 6 presents a practical Roadmap to Scale—actionable steps you can take now to translate vision into scalable value while preserving core strengths. Codifying repeatable processes helps sustain velocity as you grow the customer base.
Invest in scalable systems (CRM, marketing automation, analytics), establish a continuous learning loop with customer feedback and experimentation, and prepare for capital needs with milestone-based funding plans. A disciplined approach to growth governance, KPI tracking, and learning ensures the company remains resilient and focused on long-term impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Startup to Scaleup Growth and why is the growth lifecycle important in this journey?
Startup to Scaleup Growth describes the shift from early experimentation to scalable, governance-driven operations. The growth lifecycle outlines stages from finding product-market fit to building repeatable sales, scalable processes, and robust governance, helping founders align product, market, team, and capital as they grow.
In the Startup to Scaleup Growth framework, how do you transition from Stage 1 Startup Foundations to Stage 2 Transition to Growth?
Stage 1 focuses on finding product-market fit; Stage 2 shifts to scaling with a repeatable GTM engine. A disciplined startup growth strategy builds repeatable sales processes, pricing, onboarding, and enablement, and tracks cohort metrics such as CAC, LTV, churn, and payback period to prove scalable unit economics.
What role do growth-stage metrics play in Startup to Scaleup Growth?
Growth-stage metrics provide visibility into profitability and efficiency during scaling. They include CAC payback, gross and contribution margins by product, churn, net retention, and expansion revenue, plus run rate and runway, helping leadership spot bottlenecks and prioritize investments.
What are venture scaling strategies and how do they support Startup to Scaleup Growth?
Venture scaling strategies are deliberate approaches to grow with investor capital—pricing strategy, channel partnerships, and a teachable go-to-market motion. In Startup to Scaleup Growth, these strategies help build a scalable GTM engine and ensure repeatable, profitable growth.
How should you design teams and governance for Stage 3 Scaleup Readiness in Startup to Scaleup Growth?
Stage 3 focuses on organization design, leadership, and scalable operations. Build an org structure with product, marketing, sales, customer success, and operations; implement scalable processes and governance such as OKRs, quarterly planning, and regular business reviews to maintain velocity with discipline.
What common pitfalls should startups avoid on the path from Startup to Scaleup Growth?
Avoid over-hiring before the business model is proven and growth without solid unit economics; resist feature bloat and misalignment with core value proposition; monitor churn and customer success, and maintain disciplined KPI tracking as part of a steady governance cadence.
| Stage | Focus / Purpose | Key Actions / Milestones | Core Metrics / Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1: Startup Foundations | Find Product–Market Fit and a viable model via rapid experimentation | – Validate core value proposition with real users – Define early metrics: activation, retention, NPS – Establish lightweight customer feedback loop |
PMF proven; early pricing/packaging defined; repeatable development processes established |
| Stage 2: Transition to Growth | Shift to scalable execution with a formal GTM engine | – Define repeatable sales processes (lead qualification, pipeline stages, close rate) – Build scalable pricing model – Invest in onboarding, training, enablement – Start cohort metrics: CAC, LTV, churn, payback |
Repeatable GTM; scalable pricing; shorter time-to-value; cohort metrics in use |
| Stage 3: Scaleup Readiness | Build systems, teams, and governance for growth | – Design org structure for growth (product, marketing, sales, CS, operations) – Implement scalable processes for product, GTM, CS – Establish governance (OKRs, quarterly planning, reviews) – Invest in leadership development |
Scaled organization, repeatable processes, governance framework, strong leadership |
| Stage 4: Growth Metrics & Operational Excellence | Measure and optimize profitability, efficiency, and risk | – Track growth rate, revenue run rate; CAC payback, margins – Churn, net retention, expansion – Burn rate, runway, cash flow forecasting |
Data-driven decisions; visibility into profitability and risk; scalable operations |
| Stage 5: Avoiding Pitfalls | Mitigate common missteps in scaling | – Avoid over-hiring before the model is proven – Don’t sacrifice unit economics – Maintain product focus; avoid feature bloat – KPI discipline to guide decisions |
Reduced risk of unsustainable growth; clearer focus |
| Stage 6: Roadmap to Scale | Practical, immediate steps to implement scale-ready growth | – Codify growth model; scalable systems – Build leadership bench; talent development – Foster culture; continuous learning loop – Prepare for capital needs and milestones |
Clear path to scale; readiness for capital deployment and broader expansion |
Summary
Conclusion: The leap from startup to scaleup is a progression through a growth lifecycle. By understanding the stages—from startup foundations to scaleup governance—and applying a disciplined approach to product, GTM, people, and metrics, founders and leaders can sustain momentum without losing the qualities that initially made their company unique. The key is to align strategy with execution at every rung of the ladder, continuously refining value propositions and building scalable systems that support broader impact. Embrace the growth lifecycle as an ongoing journey, and you’ll maximize your Startup to Scaleup Growth while delivering meaningful value to customers, employees, and investors alike.