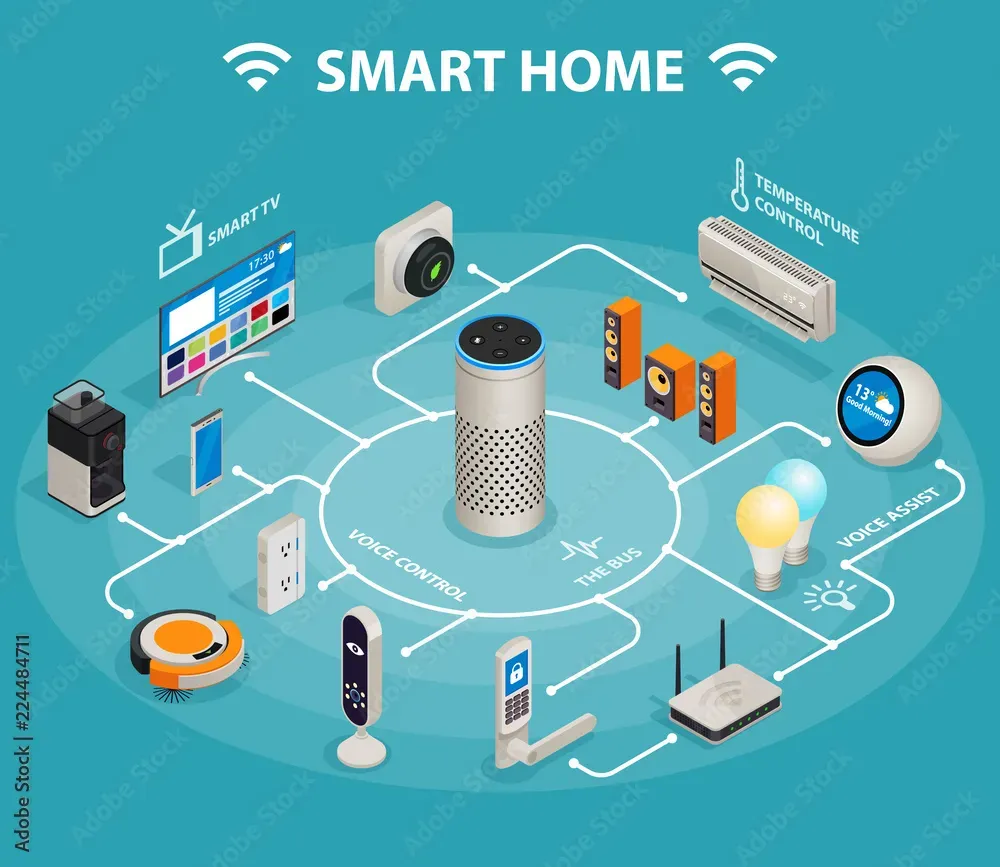
Smart Homes and IoT are reshaping how we live, turning ordinary rooms into responsive, data-driven spaces that anticipate our daily routines, adapt to our preferences, and quietly learn from our habits to simplify decisions, conserve energy, and enhance everyday comfort, especially for families, renters, and busy professionals. As everyday devices, sensors, and appliances connect through wireless networks and cloud services, including connected home devices, these ecosystems unlock convenience, real-time insights, remote management, and proactive energy awareness across every corner of the home. When paired with smart home technology, users gain effortless control over lighting, climate, entertainment, and security through intuitive apps, voice assistants, and unified dashboards that provide a seamless, personalized experience without demanding constant attention, and energy-saving modes that reduce costs without sacrificing comfort. This evolving landscape also invites careful consideration of energy efficiency in smart homes and IoT security for smart homes, shaping choices about devices, networking, data handling, and user education to maximize performance while preserving privacy and resilience. In short, a connected ecosystem learns from patterns, optimizes resource use, and enables new ways to interact with space, making homes safer, more comfortable, and capable of supporting healthier, more sustainable lifestyles.
Delving deeper, the concept can be described through terms like intelligent living environments and a network of connected devices that communicate through secure channels to streamline daily routines. Rather than a single gadget, it is an integrated home automation network where ecosystems orchestrate lights, climate, media, and access control to deliver comfort with energy awareness. From a privacy and security perspective, this shift emphasizes resilient architectures, routine software updates, and transparent data practices that build trust while enabling seamless control across multiple brands. As the space of smart living evolves, developers leverage Latent Semantic Indexing concepts to pair related ideas—like automation, sensing, and cloud processing—with user needs, ensuring content remains discoverable and coherent for readers and search engines alike.
Smart Homes and IoT: Transforming Living Spaces
Smart Homes and IoT are reshaping daily life by connecting everyday objects through the internet, turning ordinary rooms into adaptive environments. Sensors, cameras, thermostats, and appliances become part of a responsive ecosystem that learns from patterns and adapts to routines. This network of connected home devices forms the backbone of modern living and is powered by smart home technology and home automation systems that coordinate actions across brands.
From lighting to climate control to security, residents enjoy seamless control from a single interface or voice command. The result is a home that anticipates preferences, reduces manual tasks, and enhances comfort. As the ecosystem evolves, users gain deeper insights into usage and opportunities to optimize energy and security without sacrificing privacy.
Key Components of Modern Smart Home Systems
At the heart of any setup are hubs and ecosystems that act as the brain, coordinating devices across protocols. A robust platform supports a wide range of connected home devices, including smart thermostats, lighting, cameras, door locks, and sensors, forming the core of effective home automation systems.
Apps, dashboards, and voice assistants provide accessible controls, while data and analytics enable smarter decisions and energy management. This layer translates raw device data into actionable insights, supporting ongoing optimization of comfort and efficiency within the home.
Energy Efficiency in Smart Homes: Smart Automation for Lower Bills
Energy efficiency in smart homes is achieved when devices respond intelligently to occupancy, weather, and usage patterns. Smart thermostats learn routines to modulate heating and cooling, while smart plugs and energy-monitoring outlets reveal where energy is wasted. This intelligent automation aligns with broader smart home technology strategies to curb utility costs.
Automated lighting and window shades adapt to daylight, occupancy, and scenes, reducing waste without compromising experience. As a result, households see tangible utility savings while maintaining comfort and convenience, underscoring how energy efficiency in smart homes can be realized through thoughtful device orchestration.
Security and Privacy: Strengthening IoT Security for Smart Homes
IoT security for smart homes is essential as devices connect to the internet and each other. A strong foundation includes network segmentation, strong authentication, encryption, and timely firmware updates to reduce exposure windows. These practices are critical for safeguarding connected home devices and the broader smart home ecosystem.
Privacy controls and vendor transparency help users limit data collection and cloud dependencies. Regular reviews of device permissions, on-device processing, and opt-out options support safer, more private smart living, reinforcing trust in smart home technology and IoT deployments.
Interoperability and Standardization: Building a Cohesive Home Automation Platform
Interoperability ensures devices from different brands work together under a single dashboard. A cohesive platform reduces friction for expansion and helps avoid orphaned devices that break the user experience. This is a core goal for many home automation systems seeking seamless cross-brand compatibility.
Look for support of common standards and ecosystems, robust developer tools, and ongoing security updates. Standardization drives smoother integration for connected home devices and the evolution of home automation systems, making smart living more scalable and reliable.
Getting Started: A Practical Roadmap to Your Smart Home Journey
Begin with clear goals and a prioritized plan for rooms or tasks to automate, such as lighting, climate, and security. Choosing a hub or ecosystem that supports a broad range of devices sets the foundation for future growth and cross-brand compatibility, aligning with best practices in smart home technology adoption.
Start with core devices like a smart thermostat, smart lighting, and entry sensors, then add energy-monitoring and safety features over time. Emphasize energy efficiency, secure setup, and scalable architecture to keep your smart home technology future-proof, ensuring a practical, incremental path toward a connected and automated home.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Smart Homes and IoT, and how do they work together in home automation systems?
Smart Homes and IoT describe a network of connected devices that communicate over the internet or local networks to perform tasks automatically or on demand. In a home automation system, devices such as thermostats, lights, cameras, and sensors share data through a secure platform, enabling centralized control via apps or voice assistants. This integration delivers convenience, energy efficiency, improved security, and a responsive living environment powered by smart home technology.
How can I boost energy efficiency in smart homes using connected home devices?
Energy efficiency in smart homes is boosted by devices like smart thermostats, occupancy sensors, and energy-monitoring plugs that automate HVAC and lighting based on actual use. Connected home devices learn patterns, adjust behavior for occupancy and weather, and provide dashboards to track savings and optimize consumption.
What should I know about IoT security for smart homes when choosing devices?
IoT security for smart homes starts with selecting devices that support secure standards, regular firmware updates, and strong authentication. Implement network segmentation, keep firmware current, and prefer devices with privacy controls. A secure, well-managed setup across your home automation systems helps protect your data and privacy.
How do hubs and ecosystems affect Smart Homes and IoT performance?
A hub or ecosystem serves as the brain of your Smart Homes and IoT setup, coordinating connected devices across brands and protocols. This central platform improves interoperability, simplifies control, and strengthens security and energy-management capabilities within your home automation systems.
What are practical steps to start a Smart Homes and IoT journey with energy efficiency and security in mind?
Start by defining goals and selecting a scalable hub, then begin with core devices like a smart thermostat and smart lighting. Plan for energy efficiency by choosing devices that monitor and optimize usage, and prioritize security from day one by changing defaults and enabling strong authentication. Build gradually to ensure interoperability across connected home devices.
How can I manage privacy and data control across connected home devices within a Smart Homes and IoT setup?
Review data collection policies and privacy settings, opt out of non-essential sharing, and limit cloud-dependent features where possible. Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and favor devices that support encryption and clear vendor interoperability to maintain control over your smart home technology and connected devices.
| Topic | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Smart Homes and IoT turn spaces into data-driven environments by connecting devices to gather data and automate actions; benefits include convenience, energy efficiency, enhanced security, and centralized control via a single interface or voice commands. |
| What are Smart Homes and IoT? | A network of connected devices that communicate over the internet or local networks to perform tasks automatically or on demand; IoT is the broader umbrella, while smart home tech provides user-friendly interfaces and ecosystems for monitoring and control. |
| Evolution of Technology | Advances in wireless protocols (Wi‑Fi, Zigbee, Z‑Wave, Thread), sensors, cloud computing, and AI-driven automation have made a unified, scalable home ecosystem possible, enabling customization without sacrificing privacy or security when done correctly. |
| Key Components | Hubs/ecosystems; Connected devices (thermostats, lighting, cameras, locks, sensors, appliances); Apps/interfaces (dashboards, voice assistants); Data and analytics for real-time monitoring and smarter decisions. |
| Benefits | 1) Convenience and comfort through scenes and routines; 2) Energy efficiency via optimized consumption; 3) Enhanced safety with real-time alerts; 4) Asset management and maintenance with predictive insights; 5) Accessibility through voice control and inclusive interfaces. |
| Security, Privacy, and IoT Safety | Secure practices are essential: network segmentation; strong authentication and encryption; regular firmware updates; adherence to standards and interoperability; and privacy controls to review data sharing and limit cloud-dependent features. |
| Practical Steps to Start | Define goals and desired outcomes; choose a capable hub; start with core devices (thermostat, lighting, door sensor); plan for energy efficiency; expand gradually while testing interoperability; prioritize security from day one. |
| Interoperability and Cohesive Platforms | A cohesive platform enables cross-brand compatibility and centralized control, reducing friction and device orphaning; look for standards support and robust developer ecosystems when evaluating devices. |
| Real-World Scenarios | Families returning home trigger warm lighting, adjusted temperature, and a started playlist; security alerts monitor door activity; energy insights inform long-term usage optimization. |
| Future Trends | Increased edge computing, advanced AI-driven automation, Standards convergence, stronger security protocols, and deeper energy-management capabilities to broaden adoption and efficiency. |
Summary
Table provides a concise breakdown of core Smart Homes and IoT concepts with key components, benefits, security considerations, practical steps, interoperability, real-world use cases, and future directions.