Scalable Business Models for Online Entrepreneurs are not merely about pushing more sales; they are about building repeatable systems that grow with demand, preserve quality, strengthen customer relationships, and protect margins, so expansion doesn’t erode service levels, overwhelm support staff, or introduce the chaos of mismanaged scale. In 2026, online entrepreneurship thrives at the intersection of subscription businesses, SaaS for entrepreneurs, and digital product scaling, where durable value is delivered through automated workflows, self-serve onboarding, tiered access, renewal logic, and data-driven optimization that makes every new customer easier to serve while increasing lifetime value. This guide breaks down the core mechanisms—reproducible value, automated operations, sustainable unit economics, and predictable revenue—into actionable steps, from mapping the full customer journey and defining the value loop to validating pricing and packaging with lean pilots that minimize risk, test assumptions, and maximize early-life value. You’ll see practical examples across niches, including evergreen digital products, modular software, marketplaces, and content ecosystems, with emphasis on measuring key metrics like CAC, LTV, churn, activation, expansion revenue, and onboarding time so you can tune experiences, reduce friction, and scale without compromising customer happiness. By embracing a systems-based approach to growth, one that treats automation, data, and human touch as coordinated levers, online entrepreneurs can turn ambitious ideas into resilient ventures that deliver scalable outcomes, free time for strategic work, and a high bar for user experience as markets evolve.
From a semantic perspective, the topic can be framed with related terms and concepts such as scalable revenue streams for digital ventures, growth engines that operate with minimal ongoing manual effort, and platform-based ecosystems that leverage network effects to compound value. Rather than relying on a single tactic, successful online businesses hinge on repeatable processes, modular offerings, and pricing architectures that align incentives with outcomes. In practice, this means prioritizing automation, clear onboarding, and measurable health metrics that reveal when to expand features, launch new tiers, or extend support without compromising the user experience. Using varied phrasing, from growth systems for internet-based startups to scalable operations for digital commerce and revenue models with compounding value, helps align content with Latent Semantic Indexing principles while keeping the message accessible.
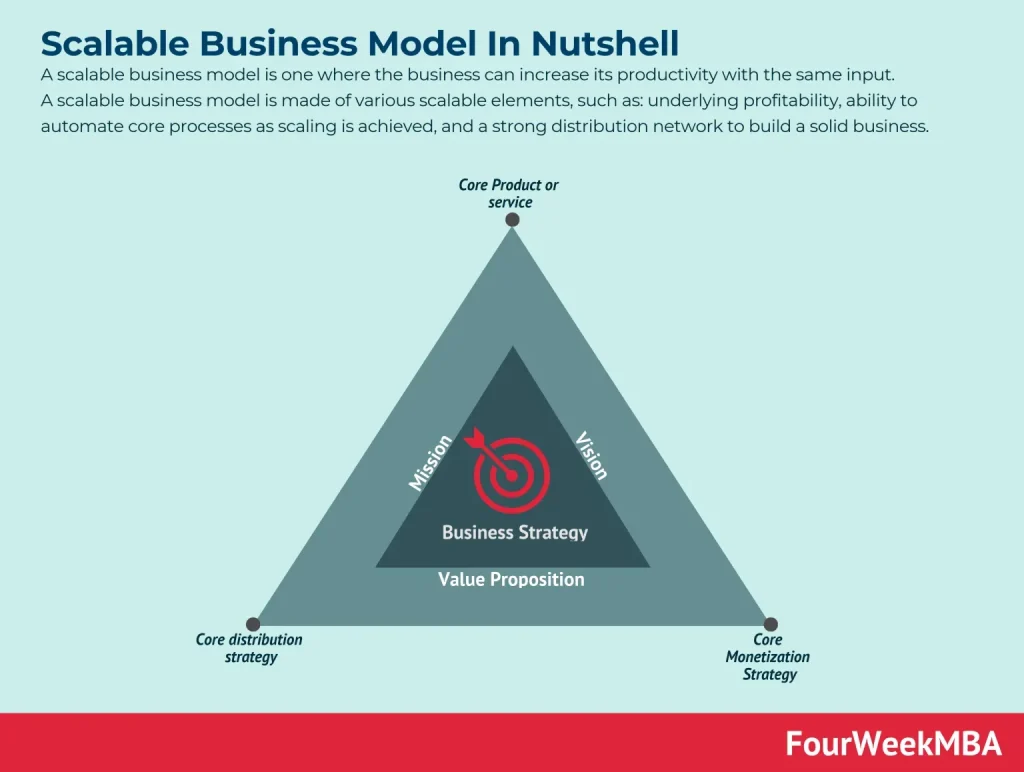
What Scalability Really Means for Online Ventures in 2026
In 2026, scalability for online ventures means more than just growing revenue; it means growing efficiently, reliably, and sustainably as demand expands. A truly scalable model can absorb more customers, handle more transactions, and manage greater complexity without a corresponding spike in cost or a dip in quality. For online entrepreneurs, this translates into systems that deliver value automatically, so effort shifts from one-off sales to repeatable, predictable revenue streams. This mindset aligns closely with the core ideas of online entrepreneurship, where the goal is to create leverage—a framework that compounds value over time rather than chasing every new launch.
To assess scalability in practice, focus on repeatable processes, onboarding friction, and customer lifetime value (LTV) over short-term wins. A scalable approach looks for automation opportunities, self-sustaining operations, and clear documentation that minimizes bespoke support. When you pair these principles with a well-defined niche, growth becomes a design choice rather than an emergency fix, enabling you to deliver consistent experiences as your audience expands.
Understanding Scalability in Action: Core Concepts for 2026
Across channels—digital products, software-as-a-service (SaaS), marketplaces, and content-driven businesses—scalability rests on a few non-negotiable foundations: reproducible value, automated operations, predictable revenue, and strong unit economics. Reproducible value means onboarding is standardized, the product experience is consistent, and support is streamlined through clear documentation. Automation frees time for strategy, while predictable revenue comes from diversified, repeatable streams. Healthy unit economics require CAC to sit below LTV, ensuring margins stay intact as marketing and support costs scale.
These principles are universally applicable to online entrepreneurship. By designing systems that deliver value at scale—whether you’re selling digital products, offering a SaaS solution, running a marketplace, or monetizing content—you create a scalable framework that can adapt to evolving markets. The focus remains tireless: reduce friction, accelerate delivery, and ensure that growth is sustainable rather than merely additive.
Scalable Business Models for Online Entrepreneurs: Core Principles and Pathways
Scalable Business Models for Online Entrepreneurs centers on four pillars: reproducible value, automated operations, predictable revenue, and strong unit economics. When value can be delivered consistently, the onboarding experience is standardized and documentation reduces the need for bespoke support. Automation handles repetitive tasks, from payments to onboarding nudges, freeing you to pursue strategic growth initiatives. Predictable revenue is built through a mix of recurring streams, with diversification reducing risk and increasing resilience.
In practice, this means embracing a portfolio that includes subscription businesses, SaaS for entrepreneurs, and digital product scaling. Each model benefits from modular pricing, clear upgrade paths, and a frictionless cancellation policy that still protects retention. The result is a scalable engine: online entrepreneurship powered by repeatable, high-value interactions rather than one-off transactions.
Designing Revenue Streams That Scale: From Subscriptions to Marketplaces
A scalable online business often combines multiple revenue streams that complement one another. Subscriptions provide steady cash flow and longer customer lifetimes, while SaaS applications enable automated fulfillment and ongoing product improvements. Digital products scale with minimal marginal cost when packaged evergreen content, templates, or courses with updates. These streams create layered value, allowing you to add revenue without proportionally increasing overhead.
Marketplaces and hybrid models further amplify scale by leveraging network effects and diversified monetization—listing fees, commissions, premium features, and access to exclusive tools. The challenge is balancing incentives so growth in supply doesn’t overwhelm demand or degrade user experience. By weaving together subscription, SaaS, digital products, and marketplace dynamics, you create a resilient ecosystem that supports online entrepreneurship across niches.
A Practical Framework to Move from Concept to Execution
Turning scalable ideas into reality requires a repeatable, data-informed process. A practical framework begins with defining the value loop—mapping the customer journey from discovery to ongoing value and identifying where automation and onboarding can reduce friction. It also calls for choosing a core model (or a combination) and validating it with a minimal-risk pilot to assess CAC, churn, onboarding time, and early-life value.
From there, you design for onboarding and retention, automate operations (payments, renewals, communications), and iterate on pricing and packaging. Scale with data by building dashboards that track key metrics like CAC, LTV, churn, activation, and expansion revenue. This framework is adaptable across niches—whether you’re a content creator, a SaaS founder, or running a marketplace—and is grounded in the idea that scalable growth is the result of deliberate, repeatable design rather than chance.
Tailoring Scalable Models Across Niches: Content, Software, and Communities
Different online niches require tailored packaging and delivery. For content creators and educators, evergreen digital products (courses, templates) paired with a subscription library can stabilize revenue while affiliates broaden reach. In the education space, retention is bolstered by content updates, live Q&A sessions, and an active community that reinforces ongoing value—key elements of scalable online entrepreneurship.
Software and SaaS founders benefit from a modular platform with core features on a subscription plus optional add-ons, emphasizing fast onboarding and transparent pricing ladders. Marketplaces and communities scale by providing low-friction entry points, premium listings, and exclusive tools, while investing in discovery and trust signals to encourage repeat participation. Across all archetypes, the objective remains: automate where it matters, deliver consistent value, and expand revenue channels without sacrificing user experience.
Trends, Signals, and a 90-Day Action Plan for 2026
Emerging trends for 2026 include AI-assisted workflows, micro-SaaS offerings, and platform-based ecosystems. More creators will monetize through memberships and licensing models, while software startups experiment with usage-based pricing and API-first strategies. The best guidance remains customer-centric: continuously measure value, automate where it matters, and iterate packaging and pricing as customer needs evolve.
A practical 90-day action plan translates these trends into a concrete, time-bound program. In weeks 1–4, validate your core model, map the value loop, and design a minimal onboarding experience. Weeks 5–8 focus on automation for payments, onboarding, and renewals, plus tiered pricing. Weeks 9–12 launch an MVP, collect feedback, and optimize retention streams, then continue to monitor CAC, LTV, churn, activation, and expansion revenue. This disciplined approach aligns with the goal of scalable, profitable growth that serves customers well and sustains the business over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are scalable business models for online entrepreneurs, and why are they essential in 2026?
Scalable business models for online entrepreneurs are systems that grow revenue efficiently through automation, repeatable value, and strong unit economics. In 2026, combining elements like subscription businesses, SaaS for entrepreneurs, and digital product scaling helps you serve more customers without a proportional rise in costs, delivering durable, data‑driven growth.
How do subscription businesses support scalable growth for online entrepreneurship?
Subscription businesses create predictable, recurring revenue and improve retention through tiered pricing and ongoing value. By automating onboarding, renewals, and support, you increase lifetime value (LTV) while reducing customer acquisition costs (CAC), aligning with scalable business models for online entrepreneurs.
What role does SaaS for entrepreneurs play in scalable business models for online entrepreneurs?
SaaS for entrepreneurs provides automated fulfillment, self‑serve onboarding, and modular pricing that scales with customer growth. It fits as a core revenue engine within scalable business models for online entrepreneurs, enabling upsells, cross‑sells, and higher gross margins while maintaining a strong customer experience.
How can digital product scaling be achieved within scalable business models for online entrepreneurs?
Digital product scaling leverages low marginal costs by packaging evergreen content (courses, templates) with updates and memberships. Delivering via downloadable assets or access libraries enables rapid expansion, cross‑selling related offerings, and improved LTV as part of scalable бизнес models for online entrepreneurs.
What are common archetypes of scalable models for online ventures like content, software, and marketplaces?
Common archetypes include evergreen digital goods with a subscription library, modular SaaS add‑ons, and marketplaces that monetize via listings or commissions. Apply scalable principles by enabling automated onboarding, ensuring strong unit economics, and balancing growth with a high‑quality user experience to avoid friction and churn.
What practical framework can online entrepreneurs use to implement scalable business models for online entrepreneurs?
Use a practical, repeatable framework: define the value loop, choose a core model (or a combo), validate with a lean MVP, design onboarding and retention, automate operations, optimize pricing and packaging, and scale with data. A 90‑day plan can help you test CAC, LTV, churn, activation, and expansion revenue while implementing scalable business models for online entrepreneurs.
| Key Point | Description | Notes / Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Definition of scalability | Scalability means growing more customers, transactions, and complexity without a proportional rise in costs, while maintaining quality and customer experience. It emphasizes efficient, reliable, and sustainable growth as demand expands. | Foundation for the rest of the model; focuses on repeating value and LTV over one-off sales. |
| Core principles | Non-negotiable bases for scalable systems: Reproducible value, Automated operations, Predictable revenue, and Strong unit economics (CAC | Applied across channels: digital products, SaaS, marketplaces, and content monetization. |
| Revenue streams that scale | Scalable models blend multiple streams to spread risk and stabilize growth. |
|
| Practical framework (7 steps) | A repeatable process to move from concept to execution and scale. |
|
| Niche implementation | Different niches require tailored packaging and delivery strategies to preserve value at scale. |
|
| Patterns and signals | Common challenges indicate where to improve: onboarding friction, churn, channel mix, and over-reliance on one acquisition channel. | Strong players diversify channels (email, social, affiliates, SEO) and emphasize value proposition that saves time or increases revenue. |
| Emerging trends | The future includes AI-assisted workflows, micro-SaaS, and platform ecosystems; memberships and licensing expand monetization options. | Adopt usage-based pricing, API-first offerings, and flexible licensing to stay customer-centric. |
| Implementation plan (90 days) | A practical timeline to validate, automate, and launch scalable revenue streams. |
|
Summary
End of table explanation of key points.