Women’s health at every life stage is a dynamic journey that benefits from proactive care, informed choices, and ongoing education. From adolescence through aging, understanding reproductive health, bone health for women, and preventive screenings helps tailor guidance to your unique needs. This guide emphasizes practical steps—nutrition, physical activity, sleep, and stress management—that support wellness across stages and align with age-appropriate screenings. By recognizing the role of prenatal and postnatal care in early family planning and the importance of menopause management later on, you can maintain vitality at every phase. Optimizing health at each life stage also means partnering with clinicians to address lifestyle factors, mental well-being, and cardiovascular risk as your needs evolve.
In other terms, female wellness evolves through key life milestones where hormonal shifts, nutrition, and activity shape outcomes. This perspective uses age-specific language and related topics—reproductive health through adolescence, bone density and heart health in adulthood, and menopause care. Framing health as a continuum helps readers connect prenatal and postnatal care, lifestyle strategies, and preventive screenings across stages. Using semantically linked terms such as lifecycle wellness for women, hormone-related aging, and age-based care supports clearer search intent. The approach remains accessible, practical, and grounded in evidence, helping readers translate science into everyday routines. Educators and clinicians can reuse these terms to build cohesive resources that cover prenatal care, postnatal recovery, menopause support, and bone health. By integrating these concepts, readers gain a holistic picture of health that spans puberty, childbearing years, midlife transitions, and later-life resilience. This framing supports inclusive, lifelong wellness for all women. The goal is to empower informed health decisions across every life stage. If you are a student or caregiver, this framework translates into practical daily routines and informed conversations with your healthcare team. Consistent attention to sleep, hydration, nutrition, and stress reduction makes this guidance actionable.
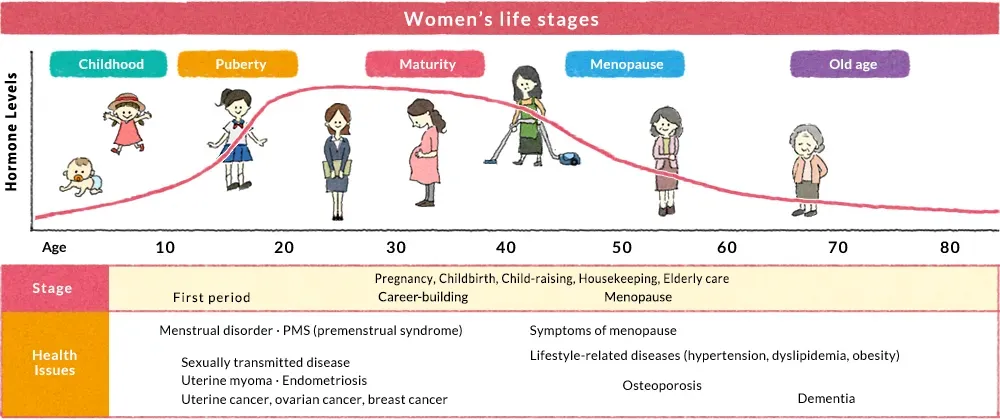
Women’s health at every life stage
A life-stage approach views health as a flowing journey through adolescence, adulthood, pregnancy, menopause, and aging. It emphasizes proactive care, prevention, and lifestyle choices that adapt to hormonal changes, body composition, and daily routines. By centering on reproductive health, bone health for women, nutrition, and physical activity, you can create a resilient foundation that supports well-being across decades.
This approach also uses personalized care from trusted clinicians, regular screenings, and informed decision-making. It highlights the importance of sleep, stress management, and mental health at every phase, while encouraging preventive care and timely vaccinations that fit your life circumstances.
Reproductive health across adolescence and adulthood
In adolescence and early adulthood, establishing healthy reproductive health practices sets the stage for years to come. Education about menstruation, contraception options, STI prevention, and consent supports autonomy and safety, while regular checks help detect issues early.
During the later reproductive years, planning for pregnancy, fertility considerations, and ongoing wellness remain central. Coordinated care with primary providers helps navigate contraception, pregnancy readiness, and routine screenings, all while keeping long-term health in focus.
Bone health for women: building strength from youth to menopause
Bone health starts in childhood and adolescence, with calcium, vitamin D, and weight-bearing activity building peak bone mass. A nutritionally rich diet and regular movement reduce future fracture risk and support energy levels.
As estrogen levels shift in perimenopause and menopause, maintaining bone density becomes a priority. Ongoing exercise, adequate calcium and vitamin D, limiting smoking and excessive alcohol, and regular bone density screening are practical steps to protect long-term bone health for women.
Prenatal and postnatal care: supporting healthy families
Prenatal and postnatal care ensures mother and baby thrive. In pregnancy, taking prenatal vitamins with folate, iron, iodine, and staying hydrated supports fetal development and maternal health, while avoiding harmful substances.
After birth, postnatal care includes lactation support, sleep strategies, mental health monitoring, and gradual return-to-routine plans. Continuity of care, including pediatric and maternal health visits, helps families establish healthy foundations and smooth transitions back to daily life.
Menopause management for lasting quality of life
Perimenopause and menopause bring hormonal shifts that affect energy, sleep, mood, and bone health. Understanding these changes and adopting lifestyle adjustments—balanced nutrition, regular activity, sleep hygiene, and stress reduction—can ease symptoms and support long-term health. This is a core aspect of menopause management.
For persistent symptoms or specific health risks, discuss options with a clinician. Treatments may include non-pharmacologic strategies, medications, and a focus on bone and cardiovascular health to support lasting quality of life.
Preventive care, screenings, and mental well-being across life stages
Regular checkups and preventive screenings are essential across life stages. An ongoing relationship with a trusted clinician helps tailor risk-based exams, cervical and breast health checks, vaccinations, and age-appropriate cancer screenings.
Mental health, nutrition, sleep, hydration, and physical activity contribute to vitality at every age. Framing these factors within the idea of women’s health at different ages emphasizes flexibility and personalized plans to address evolving needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does ‘Women’s health at every life stage’ mean, and how does it relate to women’s health at different ages?
It means proactive, stage‑specific care that evolves with hormonal changes, life events, and aging. By focusing on reproductive health, bone health for women, mental well‑being, nutrition, exercise, and preventive screenings, you can tailor care for adolescence, adulthood, pregnancy, menopause, and aging.
How can reproductive health be prioritized within women’s health at every life stage during adolescence and the reproductive years?
Prioritize education about menstruation, contraception options, STI prevention, and consent. Talk with a clinician about cervical cancer screening, and ensure HPV vaccination and other age‑appropriate vaccines are up to date to support long‑term reproductive health.
What are essential steps to support bone health for women across life stages?
Focus on adequate calcium and vitamin D, engage in weight‑bearing and resistance exercises, avoid smoking, limit alcohol, and follow bone density screening as recommended to protect bone health for women at every life stage.
What are effective strategies for menopause management as part of women’s health at every life stage?
Understand perimenopause and menopause symptoms, prioritize lifestyle factors for bone and heart health, ensure sufficient calcium and vitamin D intake, and discuss symptom management and treatment options with a clinician as needed.
Why is prenatal and postnatal care essential in women’s health at every life stage?
Prenatal care supports both maternal and fetal health through regular checkups and appropriate nutrition (including prenatal vitamins like folic acid, iodine, and iron). Postpartum care focuses on recovery, lactation support, mental well‑being, and safe return to daily routines.
What preventive screenings and general wellness steps should be part of women’s health at every life stage?
Maintain regular checkups with a trusted clinician and stay up to date with age‑appropriate screenings (cervical cancer, breast health including mammograms, cardiovascular risk, and metabolic health). Combine this with balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, hydration, and attention to mental health.
| Life Stage | Key Focus | Key Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Stage 1: Adolescence and young adulthood | Foundational health habits and reproductive health education |
|
| Stage 2: Reproductive years and family planning | Fertility optimization, pregnancy readiness, ongoing wellness |
|
| Stage 3: Pregnancy, birth, and postpartum | Prenatal care, fetal development, and postpartum recovery |
|
| Stage 4: Perimenopause and menopause management | Hormonal transitions, bone and cardiovascular health |
|
| Stage 5: Later life and aging | Maintaining independence, vitality, and social engagement |
|
| Universal strategies for every life stage | Core practices benefiting all ages |
|
Summary
Conclusion:Women’s health at every life stage emphasizes proactive, informed care that evolves with hormonal shifts, lifestyle changes, and life events. By prioritizing reproductive health, bone and cardiovascular wellness, mental well-being, and preventive care, individuals can optimize health outcomes from adolescence through aging. Embracing patient-centered care and partnering with trusted healthcare professionals—along with nourishment, movement, sleep, and consistent medical guidance—helps you cultivate vitality at every phase of life.