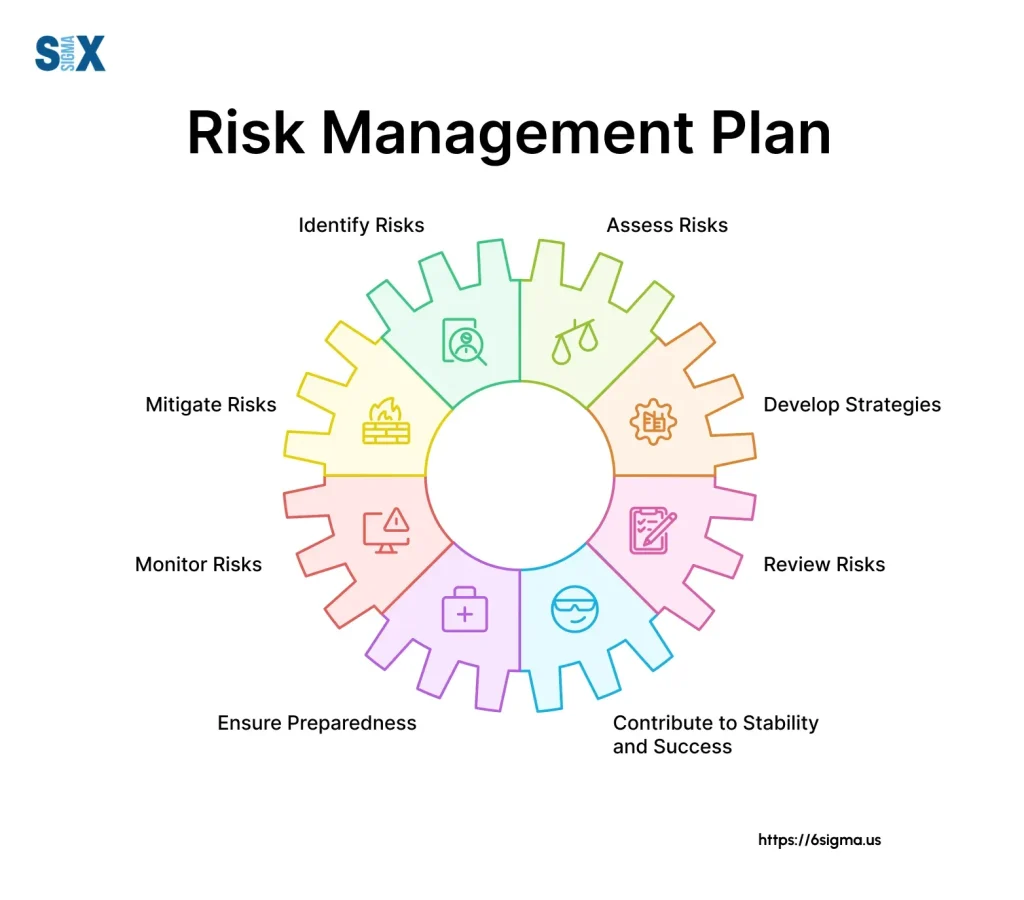
Risk Management in Business is the essential compass that helps leaders protect margins and safeguard cash flow in volatile markets, guiding strategic choices from product development to supplier selection, pricing, and investment priorities. In an era of economic swings, supply chain shocks, regulatory shifts, and evolving customer expectations, proactive planning communicates resilience, reduces ambiguity for teams, and steadies operating bets across functions. A core practice is disciplined risk management through a defined framework that assigns governance, clarifies ownership, aligns incentives, and embeds a culture that treats uncertainty as a measurable variable; this is where the concept of business risk management translates into daily action. The approach emphasizes identifying revenue levers, quantifying exposure with consistent metrics, and designing cost-efficient controls, scenario analyses, and escalation pathways that safeguard margins under pressure. With clear dashboards, timely insights, and accountable governance, organizations can enhance resilience, protect revenue, and enable smarter investments in growth while maintaining customer trust.
Viewed through an alternative lens, the same discipline is described as enterprise risk governance, uncertainty management, and resilience planning, which together capture the broader, nontechnical aspects of safeguarding value. Leaders focus on hazard mitigation, volatility forecasting, and robust controls that span operations, finance, IT, and procurement to ensure readiness without stifling innovation. By reframing risk as a strategic capability—aligning people, processes, and data around risk-aware decision making—teams communicate more clearly with stakeholders and respond quickly when disruption arises. This language shift helps cross-functional teams coordinate actions, prioritize investments, and maintain customer trust even during turbulence.
Risk Management in Business: Building Revenue Protection and Financial Resilience
Risk management in business is a continuous discipline that protects margins, preserves cash flow, and preserves strategic options. By embedding revenue protection strategies into strategy and operations, organizations cultivate financial resilience that helps weather volatility, supplier disruptions, and regulatory shifts. This approach goes beyond one-off audits, treating risk as an ongoing driver of value rather than a compliance checkpoint.
Effective risk management in business hinges on disciplined execution and a culture that translates risk insights into action. When teams align on risk indicators, governance, and accountability, they reduce the probability and severity of adverse events while accelerating recovery. The result is a more resilient organization capable of sustaining revenue growth even as external conditions shift.
Risk Assessment in Business: From Identification to Revenue Protection
A robust risk assessment in business starts with identifying revenue at risk across all parts of the organization. By mapping revenue streams, cost-to-serve, and customer credit exposure, leaders can quantify potential losses and prioritize mitigation efforts where the impact on the bottom line would be largest. This systemic view helps ensure that protections target the drivers of revenue volatility.
Quantifying risk through scenario planning, stress testing, and loss-exposure calculations turns qualitative concerns into actionable data. With clear ownership and escalation paths, risk assessment in business becomes a catalyst for timely decisions, enabling faster responses to changing conditions and helping to maintain revenue stability.
Proactive Risk Strategies for Diversified Revenue and Customer Segments
Diversifying revenue streams and customer segments is a cornerstone of proactive risk strategies. By spreading exposure across products, channels, and geographies, organizations reduce the concentration risk that can derail revenue during downturns. This approach supports more predictable cash flows and strengthens overall financial resilience.
A practical orientation toward proactive risk strategies includes flexible pricing, multi-channel distribution, and targeted customer segmentation. These measures allow firms to respond quickly to market shifts while preserving margins, ensuring revenue protection even when one segment experiences volatility.
Supply Chain Resilience: Strengthening Supplier Risk Management to Stabilize Revenue
Supplier risk management is central to revenue stability. By mapping critical suppliers, diversifying sources, and employing performance-based contracts, organizations reduce the risk of disruption to key inputs. Dual sourcing and contingency planning further shield revenue from supplier failures or price shocks.
Robust supplier risk governance and proactive monitoring—such as safety stock strategies and supplier health dashboards—enable faster recovery when disruptions occur. This emphasis on supply chain resilience protects margins by maintaining continuity of supply and reducing unexpected costs that would otherwise encroach on revenue.
Cash Flow and Liquidity Planning as Revenue Protection Strategies
Cash flow management sits at the heart of revenue protection. Rolling forecasts, enhanced accounts receivable discipline, and early payment incentives help maintain liquidity during downturns and unexpected cost spikes. These financial practices translate risk insights into proactive actions that preserve working capital and revenue generation.
Liquidity planning also encompasses contingency funding and reserve facilities to bridge short-term revenue gaps. By integrating risk data into cash flow planning, organizations can preempt liquidity crunches, reduce financing costs, and maintain operational momentum even in the face of disruption.
Cybersecurity, Data Governance, and Revenue Continuity: Protecting Value in a Digital Era
In an increasingly digital business environment, cybersecurity and data governance are essential components of revenue protection. Layered defenses, regular security assessments, and robust backup strategies minimize the likelihood and impact of breaches that could interrupt revenue streams. This aligns with broader risk management in business toward safeguarding value.
Beyond technology, governance processes and incident response planning ensure swift detection and containment of incidents. Tabletop exercises, clear ownership, and cross-functional coordination reduce downtime and protect customer trust, reinforcing financial resilience and long-term revenue continuity.
Measuring Success: Metrics, Governance, and Continuous Improvement for Risk-Aware Growth
A results-oriented approach ties risk management to revenue outcomes through clear metrics and governance. By tracking revenue-at-risk, cash conversion cycles, and escalation rates for critical dependencies, organizations can quantify the impact of risk controls and demonstrate progress toward sustainable growth. This aligns operational improvements with strategic objectives in a measurable way.
Continuous improvement—supported by regular post-event reviews and governance updates—ensures that risk management evolves with the business. Using outcomes-based indicators and feedback loops, teams refine risk controls, enhance forecasting accuracy, and strengthen financial resilience over time, reinforcing the foundation for risk-aware growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is risk management in business and why is it essential for revenue protection?
Risk management in business is an ongoing discipline that safeguards margins, protects cash flow, and preserves strategic options. It helps revenue protection by identifying threats, quantifying potential losses, and prioritizing responses before disruptions occur. A robust approach covers risk identification, risk assessment in business, mitigation, monitoring, and governance, all aligned with strategy to preserve value.
How does risk assessment in business help protect cash flow and margins?
Risk assessment in business informs where revenue is most at risk by mapping revenue streams, customer credit risk, supplier dependencies, and market exposure. It enables quantification of likelihood and impact, helping leaders protect cash flow and margins through targeted actions, contracts, and controls.
Which proactive risk strategies are most effective for building financial resilience?
Proactive risk strategies are deliberate actions that protect financial resilience and revenue when markets shift. By diversifying revenue streams, strengthening supplier resilience, sharpening pricing and terms, and improving cash flow planning, organizations fortify financial resilience while maintaining growth.
What practical steps can organizations take to implement revenue protection strategies within a risk management framework?
To implement revenue protection strategies within a risk management framework, start with a revenue-at-risk view and then: 1) map top revenue levers; 2) establish governance with clear owners; 3) develop a risk register with quantitative scores; 4) create a dedicated revenue protection playbook; 5) deploy dashboards tracking leading indicators; 6) pilot selected strategies; 7) review results quarterly.
How does a formal risk management framework support risk assessment in business and revenue protection?
A formal risk management framework supports risk assessment in business by providing a formal taxonomy, quantitative scenario analysis, governance, and structured communication. This alignment helps prioritize actions that reduce revenue at risk and strengthen overall resilience.
How can governance and monitoring improve risk management in business for sustainable growth?
Governance and monitoring strengthen risk management in business by ensuring clear ownership, escalation paths, and timely action. Real-time dashboards and key risk indicators, combined with regular reviews, help sustain financial resilience and support sustainable growth.
| Theme | Key Points / Summary | Notes / Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Nature and Purpose | Risk management is an ongoing discipline that safeguards margins, cash flow, and strategic options; requires proactive planning and a risk-aware culture. | In a rapidly changing environment, rely on processes and disciplined execution, not luck or last-minute fixes. |
| Revenue risk & importance | Helps anticipate scenarios, quantify potential losses, and protect the bottom line. | Examples: supplier failure, market downturn, cyber threats, pricing pressure. |
| Risk management framework cycle | Identify, Assess, Mitigate, Monitor, Adapt | Map revenue streams, estimate likelihood and impact, prioritize actions by revenue at risk; implement controls and dashboards. |
| Key components | Formal risk taxonomy; Quantitative analysis; Governance; Communication | Categories: strategic, financial, operational, regulatory, cyber; use scenario planning, loss exposure; assign ownership; keep stakeholders aligned. |
| Proactive strategies (overview) | Diversify revenue; strengthen supplier risk management; pricing/contract controls; cash flow management; operational resilience; cybersecurity; risk-aware culture | These form the core playbook for protecting revenue under pressure. |
| Measuring success | Connect risk activities to revenue outcomes with concrete metrics | Examples: revenue at risk (RAR); cash conversion cycle; DSO; supplier risk scores; forecast variance; incident response times |
| Practical steps to implement | Initiate risk mapping; establish governance; develop risk register; create revenue protection playbook; launch dashboards; pilot strategies; quarterly reviews | A structured rollout ensures organization-wide adoption and measurable improvements. |
| Common pitfalls | Checkbox mentality; failing to quantify risk in revenue terms; overcomplication; governance gaps | Avoid treating risk as a checkbox; ensure governance and cross-functional collaboration. |
Summary
Risk Management in Business is a discipline that extends beyond avoiding losses to enabling smarter, revenue-protecting decisions that build resilience. By embedding risk assessment into strategy, operations, and governance, organizations can anticipate disruptions, quantify potential losses, and respond with diversified revenue streams, resilient supply chains, prudent pricing, disciplined cash flow management, robust cybersecurity, and a culture of continuous improvement. This integrated approach strengthens margins, preserves cash flow, and sustains long-term value for stakeholders, even in volatile markets.