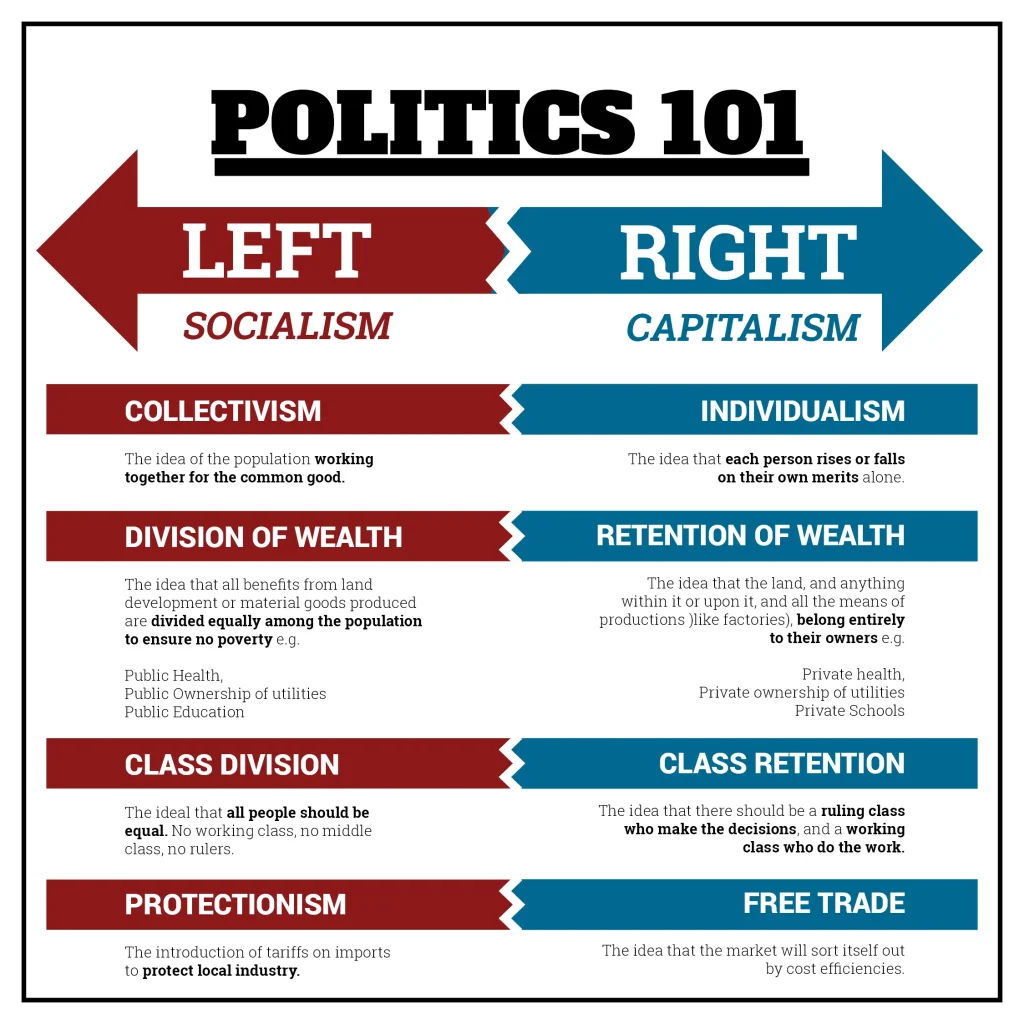
Politics 101 is a practical starting point for understanding how societies organize power, make collective decisions, and influence everyday life. As you explore government structure and how political power works, you connect headlines to the real institutions that shape policy. This introduction clarifies the roles of the branches of government and offers a clear democracy explained alongside policy-making perspective. A focus on civic participation shows how ordinary citizens can influence policy through voting, engagement, and advocacy. By linking concepts to everyday examples, the guide becomes a practical toolkit for informed participation in the political process.
Viewed through a fresh lens, governance basics resemble the architecture of public power, where ideas, rules, and institutions shape daily life. This framing shifts from a label-based approach to a concepts-based map of authority, public institutions, and citizen influence. Instead of Politics 101, think of foundational governance, the mechanics of the state, or the playbook that translates citizen needs into policy. By connecting these ideas to real processes—elections, budgeting, public meetings, and policy debates—the topic stays tangible and relevant to readers.
Politics 101: A Practical Guide to Government Structure and Power
Politics 101 is a practical starting point for understanding government structure and power. By framing politics as a process of bargaining, negotiation, and collective decision-making, readers learn where authority originates and how it flows through institutions such as legislatures, the executive, and the courts. This framework helps demystify public life, connect headlines to policy, and show how decisions about budgets, laws, and services affect daily life in homes, schools, and workplaces. Seeing the system this way makes abstract ideas concrete and empowers readers to participate more deliberately in civic life.
Across local, state, and national levels, the way power works depends on a shared architecture of institutions, norms, and rules. When a bill is proposed, the path from idea to law reveals the roles of legislators, the executive, and the judiciary. The checks and balances—vetoes, judicial review, and oversight of budgets—show how political power works in practice and why transparency matters. With this knowledge, readers can track policy, question decisions, and engage with representatives who shape the future they will inherit.
Democracy Explained: Core Features, Rights, and Everyday Life
A clear sense of democracy explained centers on participation, the rule of law, and accountable institutions functioning openly. Core features such as voting, representation, transparency, and civil liberties create a framework in which rights are protected and power is bounded. Understanding democracy explained helps readers connect classroom theory to real-world governance and see how communities shape policy through everyday political action.
Beyond formal elections, democracy involves ongoing public dialogue and informed participation. Citizens organize, debate, and monitor government performance; media and civil society provide checks that increase legitimacy. When people engage in civic participation—voting, volunteering, attending hearings, and public commentary—democracy remains a living practice that affects schools, jobs, and neighborhoods.
Branches of Government: How Laws Are Made and Policies Implemented
Branches of government form the backbone of policy-making: the legislative branch debates and passes laws, the executive implements them, and the judiciary interprets rules. This tripartite model clarifies who is responsible for each stage and why separation of powers guards rights. By seeing the roles clearly, citizens understand how a proposal becomes law and why oversight matters.
Understanding this structure also highlights the broader idea of government structure at multiple levels—local, state, and federal. The same core principles apply, even as responsibilities shift across jurisdictions. When citizens recognize the interplay among branches of government, they can better participate in debates, evaluate policy proposals, and hold leaders accountable.
Civic Participation: The Active Cornerstone of a Healthy System
Civic participation is the practical engine of democracy, inviting people to engage beyond casting ballots. Activities like attending town halls, writing to representatives, volunteering for community groups, and joining public consultations help ensure government responds to real needs and remains legitimate.
Practical tips for building a foundation include staying informed with credible sources, engaging respectfully with others, and participating at local, state, or national levels. By turning information into action—such as attending meetings or submitting feedback—citizens strengthen the system and demonstrate how everyday participation sustains public life.
Elections, Representation, and how political power works
Elections, Representation, and how political power works shows how popular will translates into policy. Elections determine who sits in office and what agendas gain the mandate to govern, while representation ensures diverse communities have a voice in lawmaking, budgeting, and oversight.
Beyond ballots, the ecosystem includes parties, interest groups, media, and civil society that influence agendas and provide checks on authority. This distribution of influence helps prevent any single actor from dominating the policy process and invites broader accountability.
Institutions, Media, and Accountability in a Healthy Democracy
Institutions, Media, and Accountability in a Healthy Democracy anchor public life. Robust courts, legislatures, and executive agencies work alongside a free, responsible press to inform citizens, scrutinize power, and invite debate. In this framework, democracy explained as a lived practice depends on reliable information and open governance.
However, challenges exist: misinformation, polarization, and closed doors can erode trust. Critical thinking, diverse sources, and active civic participation help sustain accountability and guide public action that reflects shared values.
Frequently Asked Questions
Politics 101: What is government structure and how do the three branches work together?
In Politics 101, government structure refers to how power is distributed among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Each branch has distinct roles—lawmaking, implementing policies, and interpreting laws—and checks and balances ensure no single branch dominates. Local, state, and federal levels apply the same framework, guiding how laws are made and applied across society.
Politics 101: What does democracy explained mean for citizen rights and responsibilities?
Politics 101 frames democracy explained as a system where the people influence decisions through participation, the rule of law, accountability, transparency, and equality before the law. Citizens exercise rights and responsibilities through voting, staying informed, and engaging with government to shape public policy.
Politics 101: How do the branches of government check and balance each other in practice?
The legislative, executive, and judicial branches operate with mutual oversight. Laws start in the legislature, the executive enforces them, and the judiciary reviews legality and constitutionality. This separation of powers, or checks and balances, prevents the concentration of power and protects minority rights.
Politics 101: How power works in a democracy explained, including elections and representation?
Politics 101 teaches that political power flows from voters to representatives through elections, parties, and institutions. To understand how political power works, consider how representation, interest groups, the media, and courts influence policy, and how bureaucracies implement and enforce laws. This distribution across actors is designed to balance interests and prevent concentration of power.
Politics 101: What is civic participation and why is it essential for a healthy system?
Civic participation is the active involvement of citizens in public life beyond casting ballots. It includes voting, volunteering, attending meetings, contacting representatives, and engaging in public consultations. In Politics 101 terms, active participation strengthens legitimacy, accountability, and the quality of public policy.
Politics 101: How do local, state, and federal levels fit into government structure?
Politics 101 explains that power operates at multiple levels: local handles schools and policing, state governs transportation and regulations, and the federal level sets national standards. Understanding this government structure helps citizens know where to engage and how policies travel from ideas to enacted law.
| Topic | Key Points | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| What is Politics? |
|
Shows how societies allocate resources and make collective decisions. |
| Government Structure: The Three Branches |
|
Illustrates how power is distributed and how branches check each other. |
| Checks and Balances |
|
Prevents concentration of power and maintains accountability. |
| Local, State, and Federal Roles |
|
Demonstrates multi‑level governance and where policies originate and are implemented. |
| Democracy Explained |
|
Defines how democratic systems function and what sustains legitimacy. |
| How Laws Are Made |
|
Illustrates the pathway from ideas to law and policy action. |
| Power in Politics |
|
Shows multiple channels that shape policy and public debate. |
| Civic Participation |
|
Strengthens legitimacy and accountability through active citizen involvement. |
| Institutions & Media |
|
Supports a healthy system with accountability and informed public discourse. |
| Common Pitfalls |
|
Encourages careful analysis and ongoing learning beyond slogans. |
| Practical Tips |
|
Gives actionable steps to build a solid political foundation. |