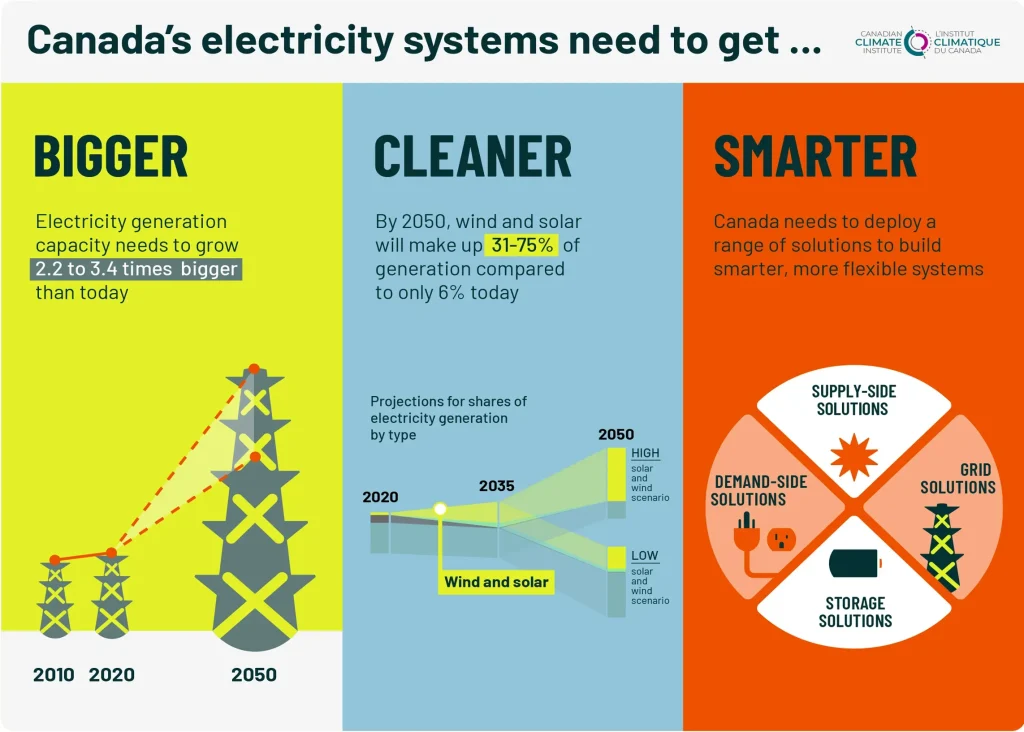
Cleaner, Smarter Grid is no distant aspiration; it is the practical mandate guiding policy, investment, and everyday energy use as we move toward World Energy 2025, shaping how homes, businesses, and networks work together more cleanly and efficiently. Across governments, utilities, and communities, the goal is to cut carbon while delivering reliable, affordable power, building trust through transparent pricing, visible performance metrics, and responsive service. The transformation relies on grid modernization—upgrading transmission and distribution with sensors, real-time data, and automated controls that shorten outage times, reduce losses, and enable rapid isolation of faults during storms and other disruptions. Renewable energy integration expands the mix of solar and wind, while storage and dynamic management keep the lights steady when conditions shift, ensuring energy security even as weather patterns evolve. Together these elements create a living system that learns from conditions, improves performance, and puts customers at the center of a cleaner energy future, powered by data-driven decisions, resilient infrastructure, and a shared commitment to a healthier planet.
This vision can also be described as a clean-energy network powered by intelligent sensing and data-driven orchestration. It represents a modernized electricity system where distributed energy resources, microgrids, and flexible storage are coordinated through advanced analytics. Rather than linear flows, the approach relies on real-time monitoring, dynamic pricing, and AI in grid management to balance supply and demand. The emphasis is on resilience, equity, and affordability as the grid becomes more participatory—consumers become prosumers, and communities benefit from smarter, more reliable power. To accelerate adoption worldwide, policymakers and industry players are embracing interoperable standards, cybersecurity, and innovative financing that support grid modernization and renewable energy integration.
World Energy 2025: Framing the Cleaner, Smarter Grid Revolution
World Energy 2025 marks a turning point where policy ambition aligns with technological capability. The pursuit of a Cleaner, Smarter Grid is no longer a niche topic but a global imperative for governments, utilities, and communities. The objective is clear: connect electricity generation with end-use demand in a way that reduces carbon intensity, enhances reliability, and enables smarter data-driven decisions that improve daily life.
This framing calls for a fundamental redesign of the power system—from one-way power flows to a dynamic, interconnected network. It requires grid modernization, renewable energy integration, and smart grid technology to create a living grid that anticipates and responds to fluctuations in supply and demand, accommodates distributed energy resources, and remains resilient against extreme weather and cyber threats.
Grid Modernization: The Infrastructure Backbone for a Cleaner, Smarter Grid
At its core, grid modernization is the infrastructure backbone of the 2025 grid. Upgrading transmission and distribution networks reduces losses, improves voltage control, and enables rapid restoration after outages. Yet modernization goes beyond new cables; it involves deploying sensors, real-time analytics, and automated controls that push the grid closer to its theoretical limits without sacrificing safety or reliability.
By enabling faster fault isolation and service restoration, modernized grids minimize downtime for homes and businesses. They also enable more efficient integration of diverse energy sources, making the system smarter, more responsive, and better able to support a future where consumers increasingly participate in energy markets and demand-response programs.
Renewable Energy Integration and Storage: Balancing a Variable World
A Cleaner, Smarter Grid must harmonize a growing share of renewable energy with the existing power system. Solar and wind bring environmental benefits but also variability. Advanced forecasting helps utilities predict resource availability and plan dispatch, while large-scale storage buffers this variability and provides emergency reserves.
Storage technologies—from conventional batteries to emerging flow systems—are critical to shifting energy to when it is most valuable. Together with grid-scale forecasting and flexible dispatch, renewable energy integration and storage reduce reliance on fossil generation while maintaining reliability and affordable prices for consumers.
AI in Grid Management: Forecasting, Optimization, and Demand Flexibility
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are moving from theory to practice in grid operations. AI-powered analytics optimize generation dispatch, detect anomalies, and guide maintenance to minimize outages. Demand flexibility becomes practical when paired with dynamic pricing, smart meters, and automated controls that steer consumption without compromising comfort or productivity.
As electrification accelerates, AI in grid management coordinates millions of devices and DERs, enabling proactive responses to changing conditions. This intelligent coordination helps prevent congestion, balance supply and demand in real time, and reduce peak demand—core elements of a smarter, more resilient grid.
DERs, Microgrids, and Local Resilience: Decentralized Power for Communities
Distributed energy resources—rooftop solar, small wind, and customer-owned storage—are redefining the traditional utility model. Effective integration requires forecasting, control software, and hardware that keep voltage and frequency stable while maximizing local value.
Microgrids offer resiliency during outages and can deliver critical services to hospitals, data centers, and essential facilities. For remote communities or campuses, microgrids illustrate a decentralized, energy-empowered approach that still harmonizes with the broader grid, reinforcing reliability while expanding control for local users.
Policy, Regulation, and Financing: Enabling Investment in a Modern Grid
The transition to a Cleaner, Smarter Grid is as much about policy and finance as technology. Regulators must create a stable investment climate, streamline permitting for transmission upgrades, standardize interconnection rules for DERs, and design rate structures that reflect the value of flexibility and resilience.
Public and private financing plays a pivotal role, with blended funding, performance-based incentives, and climate-focused subsidies helping to lower the cost of capital for advanced grid projects. Achieving equitable access to modern grid services is essential to ensure that all communities benefit from improved reliability, lower costs, and the opportunity to participate in a cleaner, smarter energy future.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does grid modernization enable a Cleaner, Smarter Grid in the context of World Energy 2025?
Grid modernization is the infrastructure backbone of a Cleaner, Smarter Grid. It upgrades transmission and distribution networks and deploys sensors, real-time analytics, and automated controls to reduce losses and enable fast fault isolation and restoration. This connectivity allows the grid to operate closer to its theoretical limits while maintaining safety, reliability, and resilience.
Why is renewable energy integration essential to achieving a Cleaner, Smarter Grid?
Renewable energy integration is central to the Cleaner, Smarter Grid by increasing environmental benefits while adding variability. The grid uses advanced forecasting and energy storage to buffer fluctuations, maintain reliability, and smooth output. Smart grid technology coordinates diverse renewable sources to deliver stable, affordable electricity.
How does smart grid technology enable AI in grid management for a Cleaner, Smarter Grid?
Smart grid technology provides the digital backbone: sensors, communication, and automation that AI in grid management uses. AI-powered analytics optimize generation dispatch, predict equipment failures, and guide maintenance, while enabling demand flexibility with dynamic pricing and automated controls. This makes the energy system proactive rather than reactive.
What does World Energy 2025 imply for implementing a Cleaner, Smarter Grid through policy and financing?
World Energy 2025 signals a shift to a dynamic, two-way grid that requires stable policy, clear interconnection rules, and supportive financing. Regulators and financiers must streamline permitting, design rates that reflect the value of flexibility and resilience, and unlock blended funding for grid modernization. Together, these steps accelerate investments in cleaner, smarter grid capabilities.
How do DERs, microgrids, and local resilience contribute to a Cleaner, Smarter Grid?
Distributed energy resources and microgrids broaden the grid’s capabilities, improving resilience during outages and reducing reliance on centralized generation. Effective integration relies on software to forecast DER output and hardware/controls to keep voltage and frequency stable. The Cleaner, Smarter Grid embraces this distributed paradigm while maintaining system-wide coordination.
What policy, regulation, and financing strategies are essential to enable a Cleaner, Smarter Grid, leveraging grid modernization and AI in grid management?
Key strategies include a stable investment climate, streamlined interconnection, transparent rate designs, and performance-based incentives that reward flexibility and resilience. Financing approaches such as blended funding and climate-focused subsidies help lower capital costs for grid modernization. Together these policies, regulations, and financing arrangements support AI-enabled grid management and a cleaner grid.
| Key Point | What it Means | Impacts / Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Connect electricity generation with end-use demand in a way that is cleaner for the planet, more reliable for consumers, and smarter in data‑driven decisions; a holistic system linking generation, transmission, distribution, and consumption. | Cleaner energy, higher reliability, smarter operations, and flexibility to accommodate diverse energy sources and consumer behaviors. | |
| World Energy 2025: fundamental redesign | Shifts from one‑way power flows to a dynamic, interconnected network where signals, energy, and information travel at scale and speed; accommodates DERs and strengthens resilience to weather and cyber threats. | More resilient, adaptable grids with lower carbon intensity and better overall performance. |
| Grid Modernization backbone | Upgrades to transmission and distribution, reduced losses, improved voltage control, and faster restoration; deployment of sensors, real‑time analytics, and automated controls. | Less downtime, improved efficiency, quicker fault isolation and service restoration. |
| Renewable Energy Integration and Storage | Harmonizing a growing share of solar and wind with forecasting, energy storage, and flexibility services to buffer variability. | Reduced fossil dependence, reliable supply, and smoother, cost‑effective energy dispatch. |
| AI, Analytics, and Demand Flexibility | AI/ML enable optimized dispatch, predictive maintenance, and demand response through pricing, smart meters, and controls. | Proactive grid management, reduced outages, and active consumer participation. |
| DERs, Microgrids, and Local Resilience | Distributed energy resources and microgrids that can operate locally and integrate with the broader system. | Enhanced resilience, energy sovereignty, and reliability, especially during outages. |
| Policy, Regulation, and Financing | Stable investment climate, streamlined permitting, interconnection rules, fair rate designs, blended financing, and climate-focused subsidies. | Faster deployment, equitable access, and lower capital costs for grid modernization. |
| Cybersecurity, Reliability, and Equity | Multi‑layer security architecture; reliability remains paramount; equitable program design for all communities. | Safer, more trustworthy grids that benefit diverse ratepayers and reduce risk. |
| Consumer Engagement and End‑User Experience | Modern metering, user-friendly dashboards, time‑of‑use pricing, and two‑way energy flows encouraging active participation. | Cost savings for customers, enhanced grid flexibility, and empowered energy users. |
| Global Collaboration | International partnerships to standardize interfaces, share pilots and data, and accelerate scalable storage and forecasting. | Faster, lower‑cost adoption of advanced grid tech through shared knowledge. |
Summary
Cleaner, Smarter Grid is shaping the future of energy systems by combining grid modernization, renewable energy integration, and smart grid technology into a resilient, affordable, low‑carbon framework. This multi‑decade journey requires coordinated action among policymakers, utilities, technology providers, and consumers worldwide. The Cleaner, Smarter Grid vision emphasizes a living, adaptive system that learns from data, adapts to changing conditions, and delivers reliable electricity with lower environmental impact. As World Energy 2025 progresses, investments in sensors, analytics, storage, electrified transport, and consumer‑centric demand management will be essential to realize a cleaner, smarter grid for all.